Moltbook, il Reddit dei Robot: Agenti AI discutono della loro civiltà (mentre noi li spiamo)
Venerdì è emersa online una notizia capace di strappare un sorriso e, subito dopo, generare un certo disagio: il lancio di Moltbook, un social network popolato non da persone ma da agenti di intellige...
Addio a NTLM! Microsoft verso una nuova era di autenticazione con kerberos
Per oltre tre decenni è stato una colonna silenziosa dell’ecosistema Windows. Ora però il tempo di NTLM sembra definitivamente scaduto. Microsoft ha deciso di avviare una transizione profonda che segn...
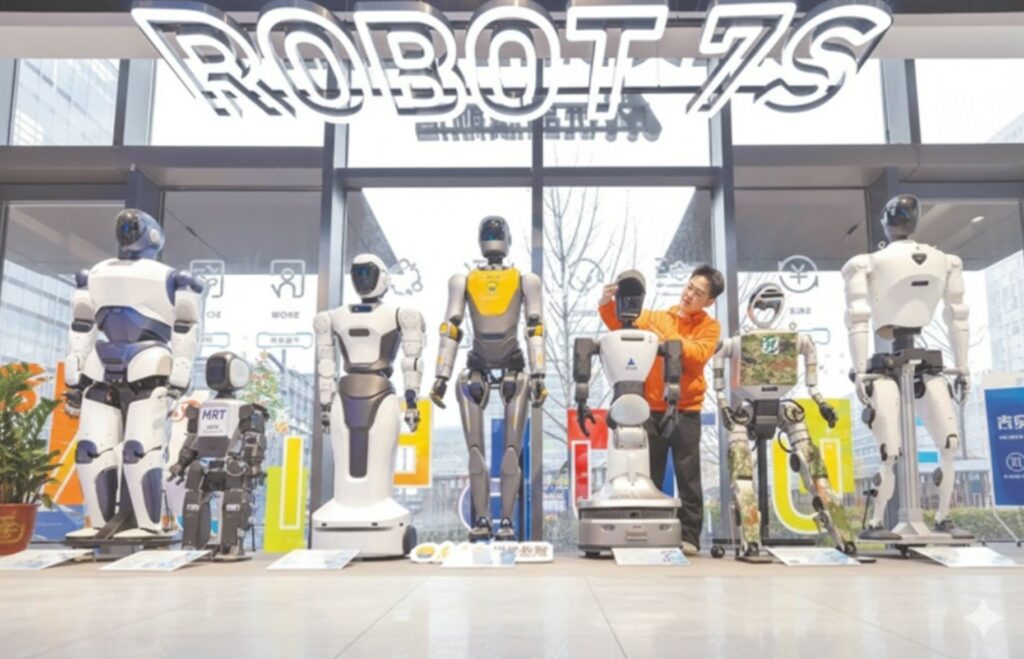
Aperti i battenti del primo negozio di robot umanoidi al mondo in Cina. Saremo pronti?
Alle dieci del mattino, a Wuhan, due robot umanoidi alti 1,3 metri iniziano a muoversi con precisione. Girano, saltano, seguono il ritmo. È il segnale di apertura del primo negozio 7S di robot umanoid...
Azienda automotive italiana nel mirino degli hacker: in vendita l’accesso per 5.000 dollari
Il 29 gennaio 2026, sul forum BreachForums, l’utente p0ppin ha pubblicato un annuncio di vendita relativo a un presunto accesso amministrativo non autorizzato ai sistemi interni di una “Italian Car Co...
Elk Cloner: Il primo virus informatico della storia nacque come uno scherzo
Alla fine degli anni 90, Internet era ancora piccolo, lento e per pochi. In quel periodo, essere “smanettoni” significava avere una conoscenza tecnica che sembrava quasi magia agli occhi degli altri. ...
Oggi nasceva Douglas Engelbart: l’uomo che ha visto e inventato il futuro digitale
Certe volte, pensandoci bene, uno si chiede come facciamo a dare per scontato il mondo che ci circonda. Tipo, clicchiamo, scorriamo, digitiamo, e tutto sembra così naturale, quasi fosse sempre stato q...
L’IA non chiede il permesso: sta riscrivendo le regole in fretta e probabilmente male
L’intelligenza artificiale è entrata nel lavoro senza bussare. Non come una rivoluzione urlata, ma come una presenza costante, quasi banale a forza di ripetersi. Ha cambiato il modo in cui le persone ...
Attenzione al “I am not a robot”: la trappola malware che usa Google Calendar
Una nuova minaccia si aggira, usando la nostra più grande debolezza: l’abitudine. Quante volte, infatti, capita di ritrovarsi a cliccare su caselle di verifica senza pensarci due volte? Ora, pare che ...
WinRAR come arma: Google scopre una falla sfruttata da APT e cybercriminali
La falla di sicurezza in WinRAR, emersa durante la scorsa estate, ha mostrato una diffusione maggiore rispetto alle aspettative. Diverse organizzazioni, sia criminali comuni che gruppi APT finanziati ...
Colpo al cuore del cybercrime: RAMP messo offline. Il “tempio” del ransomware cade!
Il forum RAMP (Russian Anonymous Marketplace), uno dei principali punti di riferimento del cybercrime underground internazionale, è stato ufficialmente chiuso e sequestrato dalle forze dell’ordine sta...
Articoli più letti dei nostri esperti
400 milioni confiscati a Helix: punizione esemplare o ultimo atto?
Carolina Vivianti - 1 Febbraio 2026
Il tuo AV/EDR è inutile contro MoonBounce: La minaccia che vive nella tua scheda madre
Bajram Zeqiri - 1 Febbraio 2026
Moltbook, il Reddit dei Robot: Agenti AI discutono della loro civiltà (mentre noi li spiamo)
Silvia Felici - 1 Febbraio 2026
I tool per di Red team si evolvono: l’open source entra in una nuova fase
Massimiliano Brolli - 31 Gennaio 2026
Addio a NTLM! Microsoft verso una nuova era di autenticazione con kerberos
Silvia Felici - 31 Gennaio 2026
Azienda italiana all’asta nel Dark Web: bastano 1.500 dollari per il controllo totale
Bajram Zeqiri - 31 Gennaio 2026
Sistemi SCADA a rischio: perché la sicurezza del file system conta più che mai
Carolina Vivianti - 31 Gennaio 2026
Vulnerabilità critica in Apache bRPC: esecuzione di comandi arbitrari sul server
Bajram Zeqiri - 31 Gennaio 2026
Aperti i battenti del primo negozio di robot umanoidi al mondo in Cina. Saremo pronti?
Carolina Vivianti - 30 Gennaio 2026
Azienda automotive italiana nel mirino degli hacker: in vendita l’accesso per 5.000 dollari
Luca Stivali - 30 Gennaio 2026
Ultime news
400 milioni confiscati a Helix: punizione esemplare o ultimo atto?
Il tuo AV/EDR è inutile contro MoonBounce: La minaccia che vive nella tua scheda madre
Moltbook, il Reddit dei Robot: Agenti AI discutono della loro civiltà (mentre noi li spiamo)
I tool per di Red team si evolvono: l’open source entra in una nuova fase
Addio a NTLM! Microsoft verso una nuova era di autenticazione con kerberos
Azienda italiana all’asta nel Dark Web: bastano 1.500 dollari per il controllo totale
Scopri le ultime CVE critiche emesse e resta aggiornato sulle vulnerabilità più recenti. Oppure cerca una specifica CVE