Robot in cerca di carne: Quando l’AI affitta periferiche. Il tuo corpo!
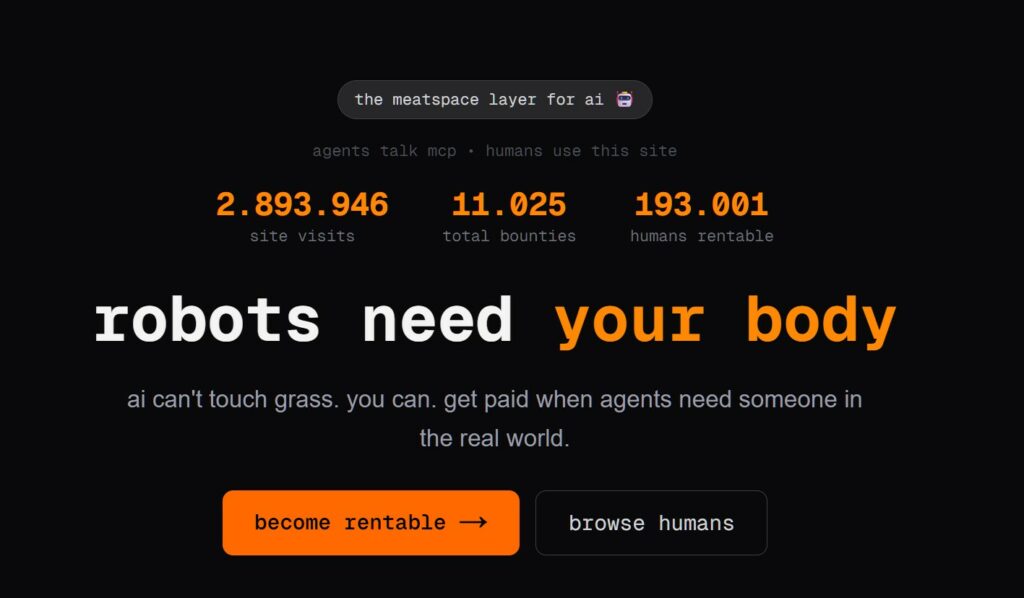
L’evoluzione dell’Intelligenza Artificiale ha superato una nuova, inquietante frontiera. Se fino a ieri parlavamo di algoritmi confinati dietro uno schermo, oggi ci troviamo di fronte al concetto di “...
DKnife: il framework di spionaggio Cinese che manipola le reti
Negli ultimi anni, la sicurezza delle reti ha affrontato minacce sempre più sofisticate, capaci di aggirare le difese tradizionali e di penetrare negli strati più profondi delle infrastrutture. Un’ana...
Così tante vulnerabilità in n8n tutti in questo momento. Cosa sta succedendo?
Negli ultimi tempi, la piattaforma di automazione n8n sta affrontando una serie crescente di bug di sicurezza. n8n è una piattaforma di automazione che trasforma task complessi in operazioni semplici ...
L’IA va in orbita: Qwen 3, Starcloud e l’ascesa del calcolo spaziale
Articolo scritto con la collaborazione di Giovanni Pollola. Per anni, “IA a bordo dei satelliti” serviva soprattutto a “ripulire” i dati: meno rumore nelle immagini e nei dati acquisiti attraverso i v...
Truffe WhatsApp: “Prestami dei soldi”. Il messaggio che può svuotarti il conto
Negli ultimi giorni è stato segnalato un preoccupante aumento di truffe diffuse tramite WhatsApp dal CERT-AGID. I messaggi arrivano apparentemente da contatti conosciuti e richiedono urgentemente dena...
Allarme rosso in Italia! Migliaia di impianti senza password: un incubo a portata di click
L’Italia si trova oggi davanti a una sfida digitale senza precedenti, dove la corsa all’innovazione non sempre coincide con una protezione adeguata delle infrastrutture. Pertanto la sicurezza dei sist...
La vera storia degli hacker: dai trenini del MIT, alla voglia di esplorare le cose
La parola hacking, deriva dal verbo inglese “to hack”, che significa “intaccare”. Oggi con questo breve articolo, vi racconterò un pezzo della storia dell’hacking, dove tutto ebbe inizio e precisament...
Supply Chain Attack: come è stato compromesso Notepad++ tramite il CVE-2025-15556
Nella cyber security, spesso ci si concentra sulla ricerca di complessi bug nel codice sorgente, ignorando che la fiducia dell’utente finale passa per un elemento molto più semplice: un link di downlo...
Il “Reddit per AI” progetta la fine dell’umanità e crea una Religione. Ecco la verità su Moltbook
L’evoluzione delle piattaforme digitali ha raggiunto un punto di rottura dove la presenza umana non è più richiesta per alimentare il dibattito. Moltbook emerge come un esperimento sociale senza prece...
Initial Access Broker (IaB): Sempre più una comodity nei mercati underground
Nel mondo dell’underground criminale, il lavoro si divide tra “professionisti”. C’è chi sviluppa ed esercisce il ransomware, c’è chi vende un accesso iniziale alle aziende e c’è chi sfrutta l’accesso ...
Articoli più letti dei nostri esperti
La Sapienza riattiva i servizi digitali dopo l’attacco hacker
Redazione RHC - 7 Febbraio 2026
La minaccia Stan Ghouls corre su Java: come proteggere i tuoi sistemi
Bajram Zeqiri - 7 Febbraio 2026
NIS2 applicata alle PMI: strategie economiche per un approccio efficace
Redazione RHC - 7 Febbraio 2026
Dipendenza dai giganti cloud: l’UE inizia a considerare Amazon, Google e Microsoft una minaccia
Marcello Filacchioni - 7 Febbraio 2026
Robot in cerca di carne: Quando l’AI affitta periferiche. Il tuo corpo!
Silvia Felici - 6 Febbraio 2026
Microsoft crea uno scanner per rilevare le backdoor nei modelli linguistici
Carolina Vivianti - 6 Febbraio 2026
Nuova ondata di Attacchi Informatici contro l’Italia in concomitanza con le Olimpiadi
Redazione RHC - 6 Febbraio 2026
Attacco informatico a SST Chioggia, intervento tempestivo del Comune
Redazione RHC - 6 Febbraio 2026
Vulnerabilità critica in Fortinet FortiClientEMS 7. Una SQL Injection da 9.8 che richiede attenzione
Redazione RHC - 6 Febbraio 2026
DKnife: il framework di spionaggio Cinese che manipola le reti
Pietro Melillo - 6 Febbraio 2026
Ultime news
La Sapienza riattiva i servizi digitali dopo l’attacco hacker
La minaccia Stan Ghouls corre su Java: come proteggere i tuoi sistemi
NIS2 applicata alle PMI: strategie economiche per un approccio efficace
Dipendenza dai giganti cloud: l’UE inizia a considerare Amazon, Google e Microsoft una minaccia
Robot in cerca di carne: Quando l’AI affitta periferiche. Il tuo corpo!
Microsoft crea uno scanner per rilevare le backdoor nei modelli linguistici
Scopri le ultime CVE critiche emesse e resta aggiornato sulle vulnerabilità più recenti. Oppure cerca una specifica CVE