
A new ad posted on an underground forum was recently spotted by researchers at the Dark Lab threat intelligence laboratory , clearly demonstrating how active and dangerous the black market for access to sensitive computer systems still is.
User “nixploiter” , with an already established profile in the underground community ( gigabyte level, with over 150 posts), recently put up for sale access to more than 1000 POS (Point of Sale) machines located between the USA and the UK .
Disclaimer: This report includes screenshots and/or text from publicly available sources. The information provided is for threat intelligence and cybersecurity risk awareness purposes only. Red Hot Cyber condemns any unauthorized access, improper dissemination, or misuse of this data. It is currently not possible to independently verify the authenticity of the information reported, as the organization involved has not yet released an official statement on its website. Therefore, this article should be considered for informational and intelligence purposes only.
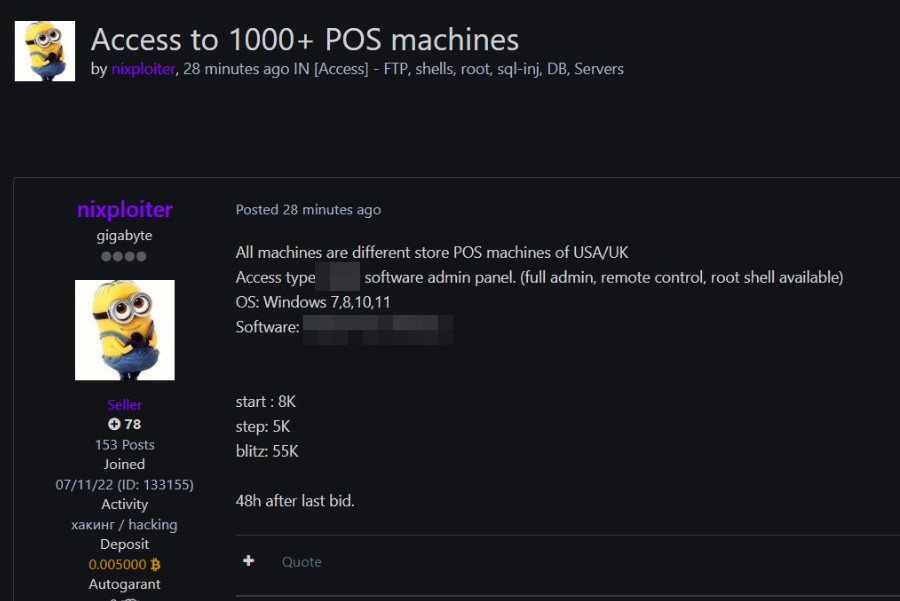
In the post, the malicious actor claims to have access via Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) administration panels , which would grant full administrative privileges , remote control , and even root shell access . The compromised machines would run Windows 7, 8, 10, and 11 systems, using software that is well-known and widely used in the retail sector.
The bidding, set up as an auction, starts at $8,000, with increments of $5,000 and an immediate “blitz” price of $55,000. The seller also sets a 48-hour window after the last bid to complete the transaction, requiring a small deposit in Bitcoin to confirm the buyer’s credibility.
Such access poses a serious direct threat not only to the stores involved, but also to customers and the connected financial networks .
POS systems handle extremely sensitive data—transactions, payment cards, credentials, and network logs—that can be exploited for:
The reference to the use of RMM software, which is common in legitimate corporate infrastructures, suggests that attackers exploited unsecured or misconfigured remote management tools —a rapidly growing technique in the threat landscape.
This episode once again highlights the importance of POS device security , which is often overlooked compared to other IT systems.
It is essential that companies:
The sale of access to over a thousand POS terminals isn’t just an isolated criminal operation: it’s an indicator of systemic vulnerability that directly affects the security of global digital commerce.
Follow us on Google News to receive daily updates on cybersecurity. Contact us if you would like to report news, insights or content for publication.
