A criminal hacker group calling itself Radiant has claimed responsibility for stealing the personal data of over 8,000 children enrolled in daycare centers run by London-based Kido International . The...
Artificial intelligence is no longer a futuristic concept from science fiction films . It is already part of our daily lives and, above all, it is revolutionizing the world of...
In recent years, the marketing industry has undergone a radical transformation : today, one in two positions requires artificial intelligence skills. According to representatives from the agency Digital Duke, the...
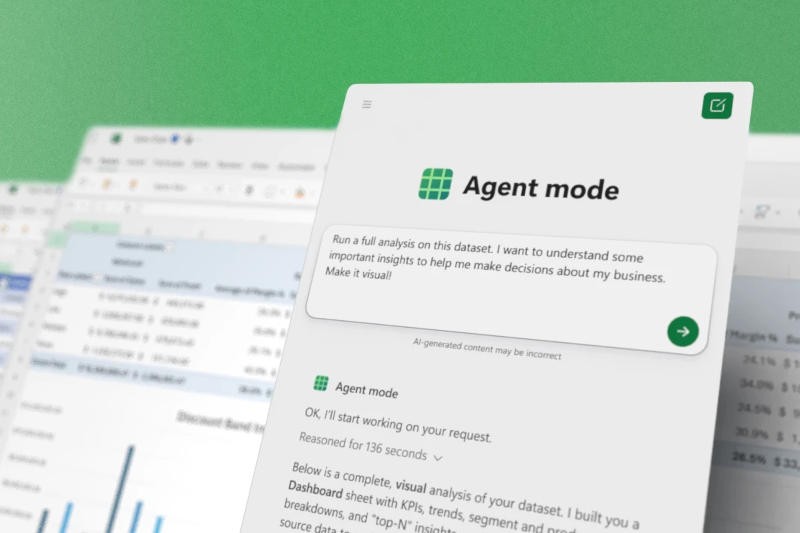
Microsoft has launched Agent Mode, an AI-powered feature in Excel and Word that automatically creates complex spreadsheets and text documents with a single text query. Copilot Chat also launched Office...
In an industry once dominated by live-action stars, digital characters are increasingly gaining traction. At a summit in Zurich, actress, comedian, and technologist Ellin van der Velden announced that her...
In recent years, many companies have gone cloud-first , outsourcing critical infrastructure and business services to platforms managed by external providers. However, recent events and growing concerns about digital sovereignty...
In recent years, cyberattacks have become a major threat to businesses, regardless of industry. While technical departments focus on troubleshooting and restoring systems, the true test of an organization's ability...
The cybersecurity industry is undergoing a transformation: artificial intelligence is becoming not just a tool for developers, but also a weapon for attackers. And we've talked about this extensively. This...
Alarming trends are emerging in the IT job market. More and more computer science graduates are unable to find work, even at minimum wage. A computer science degree was once...
The U.S. Department of Justice has received court authorization to conduct a remote inspection of Telegram's servers as part of an investigation into child exploitation. The prosecutor's motion stated that...