
Starting September 1, 2025, all artificial intelligence (AI)-generated content in China must be marked with an “electronic watermark,” according to new legislation. The stated goal is to improve the transparency of digital content and reduce the spread of false information.
In March this year, the Cyberspace Administration of China (CAC) , together with four other departments, released the “Measures for Identifying Artificial Intelligence-Generated Synthetic Content” (known as the “Identification Measures” ).
According to these rules, text, images, audio, video, and virtual scenes created using AI must carry both explicit identifiers, visible to users, and implicit identifiers, embedded in the data that produces the content.
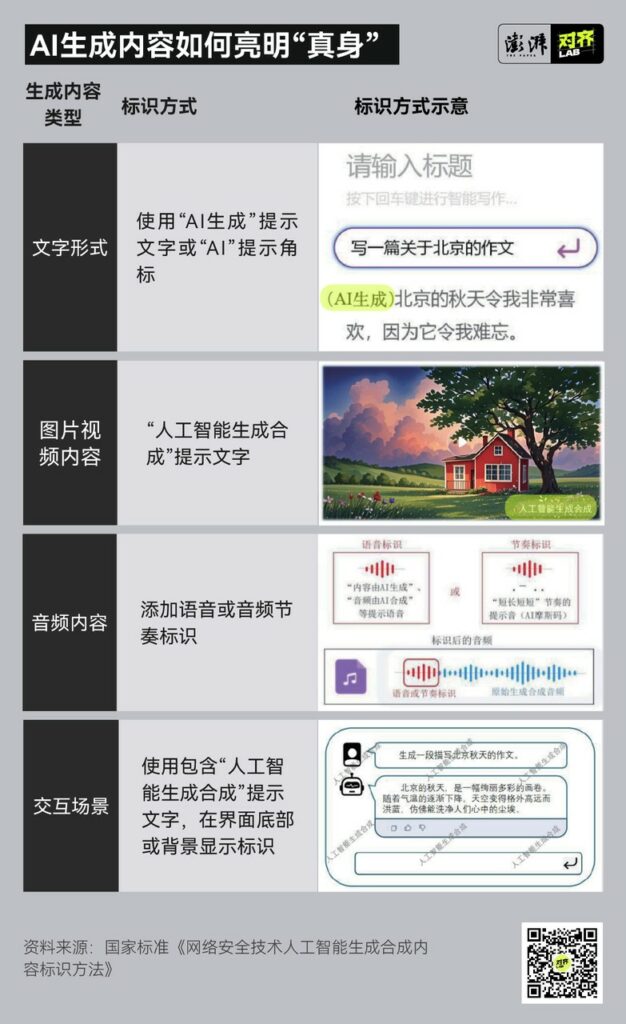
Social media platforms, including Bilibili, Douyin, Weibo, and Xiaohongshu , require publishers to proactively flag AI-generated content. Users or publishers who fail to comply risk penalties ranging from traffic restrictions to content removal and account bans . Notably, Douyin has also imposed earnings suspensions and a reduction in followers for those who fail to properly label AI content.
Many platforms have introduced “automated labeling” systems to handle unlabeled content, but their effectiveness is limited. Journalists searching for terms like “AI imagery” still found a significant amount of unlabeled AI-generated content . Some platforms initiated these rules even before the new measures were issued, demonstrating that labeling AI content is a lengthy and complex process.
According to Yao Zhiwei , professor of law at Guangdong University of Finance and Economics, the new regulations require high technical skills and it remains uncertain whether small and medium-sized platforms will be able to fully comply with them.
Publishers’ failure to report AI content is often driven by economic reasons, such as increased traffic, new account creation, and content monetization. Studies on the impact of reporting deepfakes suggest that, while reminders to users can increase awareness, they also reduce the likelihood of sharing the content.
Platforms have an ambivalent relationship with AI: on the one hand, they encourage the creation of AI-generated content, increasing traffic and promotion; on the other, they face abuse, including the spread of misinformation, pornographic content, and image and face manipulation.
In April 2025, the CAC launched a three-month special campaign , “Clear and Clear: Rectifying the Abuse of AI Technology.” The Shanghai Cyberspace Administration coordinated the actions of 15 key platforms, including Xiaohongshu, Bilibili, and Pinduoduo, intercepting over 820,000 illegal pieces of content , deleting 1,400 accounts , and removing more than 2,700 non-compliant AI entities . These actions significantly reduced the online presence of illegal AI content.
Weekly reports from platforms, such as “Clear and Bright: Rectifying the Abuse of AI Technology,” highlight the most common types of abuse: misleading advertising, vulgar content, illegal marketing of AI products, and illicit face and voice swapping. Bilibili also reports violations related to fake videos on international military issues, educational content featuring virtual experts, time travel stories, and AI models for university exam preparation.
According to the Shanghai Internet Information Office , platforms such as Xiyu Technology, Jieyuexingchen, Tongyi, Xiaohongshu, Bilibili, and Soul have nearly completed the implementation of explicit identification specifications, accelerating the development of implicit identification and communication chain verification systems. Xiaohongshu has also led the creation of a practical guide for image metadata recognition. These efforts have yielded gradual but concrete results in the management of AI-generated content.
Follow us on Google News to receive daily updates on cybersecurity. Contact us if you would like to report news, insights or content for publication.
