
Sygnia segnala che il vettore di attacco iniziale di Fire Ant CVE-2023-34048, sfrutta la vulnerabilità di scrittura fuori dai limiti nell’implementazione del protocollo DCERPC di vCenter Server che consente l’esecuzione di codice remoto non autenticato. I ricercatori di sicurezza hanno identificato arresti anomali sospetti del processo ‘vmdird‘ sui server vCenter, indicando lo sfruttamento di questa vulnerabilità critica.
Dopo aver ottenuto la compromissione, gli autori della minaccia implementano strumenti sofisticati, tra cui lo script open source vCenter_GenerateLoginCookie.py, per falsificare i cookie di autenticazione e aggirare i meccanismi di accesso. Gli aggressori raccolgono sistematicamente le credenziali vpxuser, ovvero account di sistema creati automaticamente da vCenter con privilegi amministrativi completi sugli host ESXi.
Questo furto di credenziali consente lo spostamento laterale nell’intera infrastruttura di virtualizzazione, poiché gli account vpxuser restano esenti dalle restrizioni della modalità di blocco. Gli autori della minaccia sfruttano anche il CVE-2023-20867, una vulnerabilità di VMware Tools che consente l’esecuzione di comandi host-to-guest non autenticati tramite il cmdlet Invoke-VMScript di PowerCLI.
Fire Ant dimostra notevoli capacità di persistenza attraverso molteplici tecniche di distribuzione di backdoor. Il gruppo installa vSphere Installation Bundle (VIB) dannosi con livelli di accettazione impostati su “partner” e distribuiti utilizzando il flag -force per ignorare la convalida della firma. Questi VIB non autorizzati contengono file di configurazione che fanno riferimento a file binari nella cartella ‘/bin‘ e script personalizzati incorporati in ‘/etc/rc.local.d/’ per l’esecuzione all’avvio.
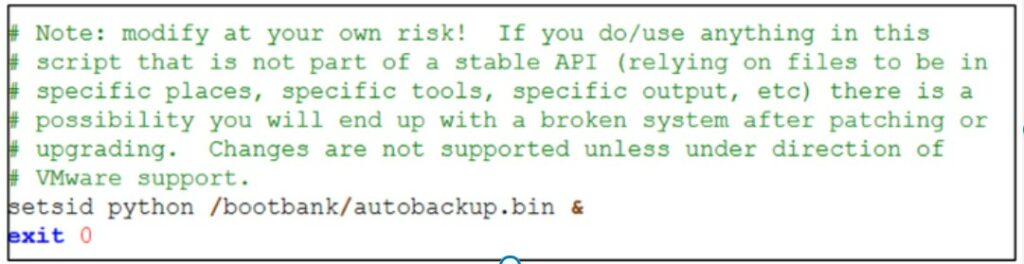
Inoltre, gli aggressori implementano una backdoor HTTP basata su Python denominata autobackup.bin che si collega alla porta 8888 e fornisce funzionalità di esecuzione di comandi remoti. Questo malware modifica ‘/etc/rc.local.d/local.sh’ sugli host ESXi per un’esecuzione persistente. Per eludere ulteriormente il rilevamento, Fire Ant termina il processo vmsyslogd, il demone syslog nativo di VMware, disabilitando di fatto sia la scrittura dei log locali che l’inoltro dei log remoti.
Gli autori della minaccia dimostrano sofisticate capacità di manipolazione della rete compromettendo i bilanciatori di carico F5 tramite lo sfruttamento CVE-2022-1388 e distribuendo webshell su ‘ /usr/local/www/xui/common/css/css.php ‘ per il bridging di rete. Utilizzano webshell di tunneling Neo-reGeorg su server web interni basati su Java e distribuiscono il rootkit Medusa su punti pivot Linux per la raccolta delle credenziali e l’accesso persistente.
Fire Ant utilizza i comandi netsh portproxy per l’inoltro delle porte attraverso endpoint attendibili, aggirando di fatto gli elenchi di controllo degli accessi e le restrizioni del firewall. Il gruppo sfrutta inoltre il traffico IPv6 per aggirare le regole di filtraggio incentrate su IPv4, dimostrando una conoscenza approfondita degli ambienti di rete dual-stack e delle comuni lacune di sicurezza nelle infrastrutture organizzative.
Le organizzazioni devono dare urgentemente priorità alla protezione dei propri ambienti VMware tramite l’applicazione completa di patch, un monitoraggio avanzato delle attività dell’hypervisor e l’implementazione di funzionalità di rilevamento avanzate che vadano oltre le tradizionali soluzioni di sicurezza degli endpoint.
Ti è piaciuto questo articolo? Ne stiamo discutendo nella nostra Community su LinkedIn, Facebook e Instagram. Seguici anche su Google News, per ricevere aggiornamenti quotidiani sulla sicurezza informatica o Scrivici se desideri segnalarci notizie, approfondimenti o contributi da pubblicare.
 Cybercrime
CybercrimeLe autorità tedesche hanno recentemente lanciato un avviso riguardante una sofisticata campagna di phishing che prende di mira gli utenti di Signal in Germania e nel resto d’Europa. L’attacco si concentra su profili specifici, tra…
 Innovazione
InnovazioneL’evoluzione dell’Intelligenza Artificiale ha superato una nuova, inquietante frontiera. Se fino a ieri parlavamo di algoritmi confinati dietro uno schermo, oggi ci troviamo di fronte al concetto di “Meatspace Layer”: un’infrastruttura dove le macchine non…
 Cybercrime
CybercrimeNegli ultimi anni, la sicurezza delle reti ha affrontato minacce sempre più sofisticate, capaci di aggirare le difese tradizionali e di penetrare negli strati più profondi delle infrastrutture. Un’analisi recente ha portato alla luce uno…
 Vulnerabilità
VulnerabilitàNegli ultimi tempi, la piattaforma di automazione n8n sta affrontando una serie crescente di bug di sicurezza. n8n è una piattaforma di automazione che trasforma task complessi in operazioni semplici e veloci. Con pochi click…
 Innovazione
InnovazioneArticolo scritto con la collaborazione di Giovanni Pollola. Per anni, “IA a bordo dei satelliti” serviva soprattutto a “ripulire” i dati: meno rumore nelle immagini e nei dati acquisiti attraverso i vari payload multisensoriali, meno…