Nel sempre più vasto mondo dell’intelligenza artificiale (IA), esiste una tecnologia rivoluzionaria che ha cambiato il modo in cui le macchine “vedono” e “comprendono” il mondo intorno a loro: le Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN).
Questi potenti algoritmi hanno aperto nuove frontiere nelle scienze informatiche, rendendo possibile ciò che un tempo era considerato fantascienza.
Ma cosa sono esattamente le CNN e come funzionano? Preparati a scoprire tutto questo nel nostro viaggio attraverso la storia, i concetti fondamentali e le applicazioni di questa affascinante tecnologia.
Le Convolutional Neural Networks, come molte delle migliori invenzioni dell’umanità, non sono nate in un giorno. Il loro sviluppo ha avuto inizio negli anni ’80 con il lavoro di un pioniere dell’IA, Kunihiko Fukushima, che ha sviluppato una rete neurale chiamata “Neocognitron”. Questa prima incarnazione delle CNN era rudimentale, ma ha gettato le basi per gli sviluppi futuri.
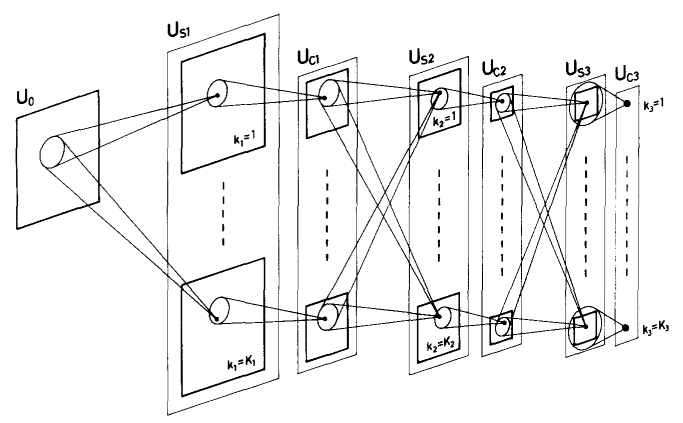
Tuttavia, il vero successo delle CNN è arrivato nel 1998, quando il ricercatore Yann LeCun ha introdotto un modello di rete neurale chiamato “LeNet-5”. Questa rete è stata utilizzata con successo per il riconoscimento di cifre scritte a mano, mostrando al mondo le incredibili potenzialità delle CNN. Da allora, grazie alla crescente disponibilità di dati e alla potenza di calcolo, le CNN sono diventate uno strumento chiave nella cassetta degli attrezzi dell’IA.
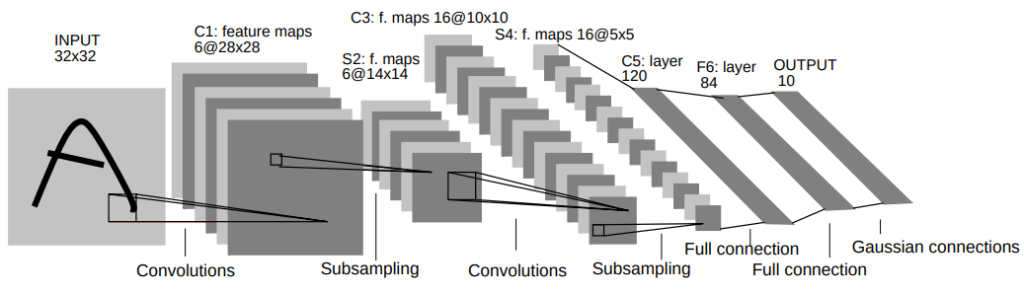
Le Convolutional Neural Networks appartengono alla famiglia delle reti neurali artificiali, un tipo di modello di apprendimento automatico che si ispira al funzionamento del cervello umano. Queste reti sono composte da neuroni artificiali o “nodi” organizzati in diversi strati.
Ciò che rende uniche le CNN è il modo in cui gestiscono le immagini. Invece di prendere un’immagine come un intero, le CNN la scompongono in parti più piccole e le analizzano strato per strato. Questo processo di “convoluzione” permette alla rete di rilevare caratteristiche locali nelle immagini, come linee, forme o colori. Queste caratteristiche vengono poi combinate nei successivi strati per riconoscere forme più complesse.
Un altro concetto fondamentale nelle CNN è il “pooling” o “subsampling”, un processo che riduce la dimensione dell’immagine mantenendo solo le informazioni più importanti. Questo rende la rete più efficiente e riduce il rischio di sovradattamento, un problema comune nell’apprendimento automatico quando il modello diventa troppo specifico per i dati di addestramento e non riesce a generalizzare bene a nuovi dati.
Le CNN includono anche strati “fully connected” o “densi”, dove ogni neurone è collegato a tutti gli altri neuroni dello strato successivo. Questi strati sono spesso usati alla fine della rete per compiere la classificazione finale, basata sulle caratteristiche rilevate dai precedenti strati convoluzionali e di pooling.
La vera forza delle Convolutional Neural Networks sta nella loro versatilità. Grazie alla loro capacità di rilevare e classificare pattern complessi nelle immagini, le CNN trovano applicazione in numerosi campi.
Riconoscimento delle immagini e della voce: Le CNN sono ampiamente utilizzate per il riconoscimento di immagini e di voce. Ad esempio, i servizi di riconoscimento facciale di Facebook o i sistemi di assistenza vocale come Siri e Alexa si basano sulle CNN.
Guida autonoma: Le CNN giocano un ruolo fondamentale nella guida autonoma. Aiutano i veicoli a “vedere” e a capire l’ambiente circostante, consentendo loro di navigare in sicurezza.
Diagnostica medica: Nel campo della medicina, le CNN stanno rivoluzionando la diagnostica. Sono utilizzate per analizzare immagini mediche, come radiografie o scansioni MRI, e possono rilevare anomalie come tumori o malattie cardiache con una precisione che rivalizza con quella dei medici umani.
Le Convolutional Neural Networks sono un potente strumento che ha rivoluzionato il campo dell’intelligenza artificiale. Hanno permesso alle macchine di “vedere” e “comprendere” il mondo in modi mai pensati prima. Ma la nostra esplorazione delle CNN è appena iniziata. Nel prossimo articolo, esploreremo più in profondità come funzionano le CNN, esaminando i dettagli tecnici dietro questi affascinanti algoritmi.
Per approfondire ulteriormente l’argomento delle Convolutional Neural Networks, vi consigliamo di consultare il corso gratuito dell’università di Stanford: Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Recognition.
Ti è piaciuto questo articolo? Ne stiamo discutendo nella nostra Community su LinkedIn, Facebook e Instagram. Seguici anche su Google News, per ricevere aggiornamenti quotidiani sulla sicurezza informatica o Scrivici se desideri segnalarci notizie, approfondimenti o contributi da pubblicare.
 Cybercrime
CybercrimeLe autorità tedesche hanno recentemente lanciato un avviso riguardante una sofisticata campagna di phishing che prende di mira gli utenti di Signal in Germania e nel resto d’Europa. L’attacco si concentra su profili specifici, tra…
 Innovazione
InnovazioneL’evoluzione dell’Intelligenza Artificiale ha superato una nuova, inquietante frontiera. Se fino a ieri parlavamo di algoritmi confinati dietro uno schermo, oggi ci troviamo di fronte al concetto di “Meatspace Layer”: un’infrastruttura dove le macchine non…
 Cybercrime
CybercrimeNegli ultimi anni, la sicurezza delle reti ha affrontato minacce sempre più sofisticate, capaci di aggirare le difese tradizionali e di penetrare negli strati più profondi delle infrastrutture. Un’analisi recente ha portato alla luce uno…
 Vulnerabilità
VulnerabilitàNegli ultimi tempi, la piattaforma di automazione n8n sta affrontando una serie crescente di bug di sicurezza. n8n è una piattaforma di automazione che trasforma task complessi in operazioni semplici e veloci. Con pochi click…
 Innovazione
InnovazioneArticolo scritto con la collaborazione di Giovanni Pollola. Per anni, “IA a bordo dei satelliti” serviva soprattutto a “ripulire” i dati: meno rumore nelle immagini e nei dati acquisiti attraverso i vari payload multisensoriali, meno…