
An Android banking Trojan and RAT called Klopatra masquerades as an IPTV and VPN app and has already infected over 3,000 devices . The malware is a Trojan capable of monitoring the device’s screen in real time, intercepting input, simulating gesture navigation, and features a stealth VNC (Virtual Network Computing) mode.
Cleafy , the company that discovered the malware, notes that the Trojan is not associated with any documented Android malware family and appears to be the work of a Turkish hacking group.
Klopatra is designed to steal banking credentials via overlays, steal clipboard contents and intercept keystrokes, steal victim accounts via VNC, and collect information about cryptocurrency wallet applications.
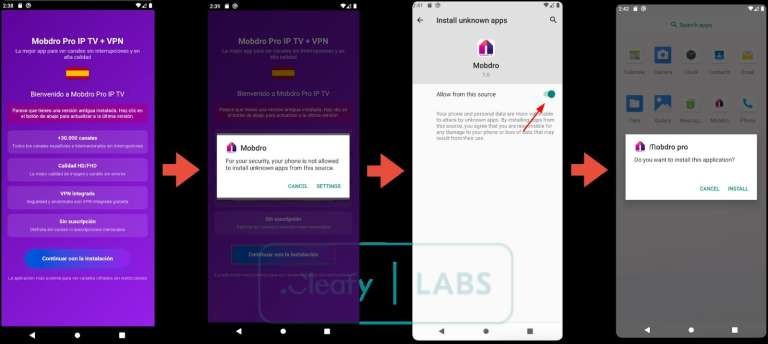
The malware infiltrates victims’ devices via a dropper app called Modpro IP TV + VPN, which is distributed outside the official Google Play store.
Klopatra uses Virbox (a commercial product that makes reverse engineering and analysis difficult), uses native libraries to reduce the Java/Kotlin footprint, and encrypts strings using NP Manager.
The RAT misuses Android’s Accessibility Service to gain additional permissions, intercept user input, simulate touches and gestures, and monitor the victim’s device’s screen to obtain passwords and other sensitive information.
One of the malware’s key features is its black-screen VNC mode, which allows Klopatra’s operators to perform actions on the infected device. To the user, the device appears idle and with a locked screen.
This mode supports all the remote actions needed to perform manual banking transactions, including simulating taps on specific areas of the screen, swipes up and down, and long presses.
To choose the ideal time to activate VNC mode, the malware checks whether the device is charging and whether the screen is off, so the user won’t suspect anything. To avoid detection, Klopatra contains an encrypted list of package names from popular Android antivirus programs and attempts to remove them.
Cleafy specialists have discovered several malware command-and-control servers. They are believed to be linked to two separate campaigns, which have already caused over 3,000 unique infections.
According to researchers, Klopatra has been active since March 2025, and during this time, about 40 different builds of the Trojan have been released, which indicates active development and rapid evolution of the new banker.
Follow us on Google News to receive daily updates on cybersecurity. Contact us if you would like to report news, insights or content for publication.
