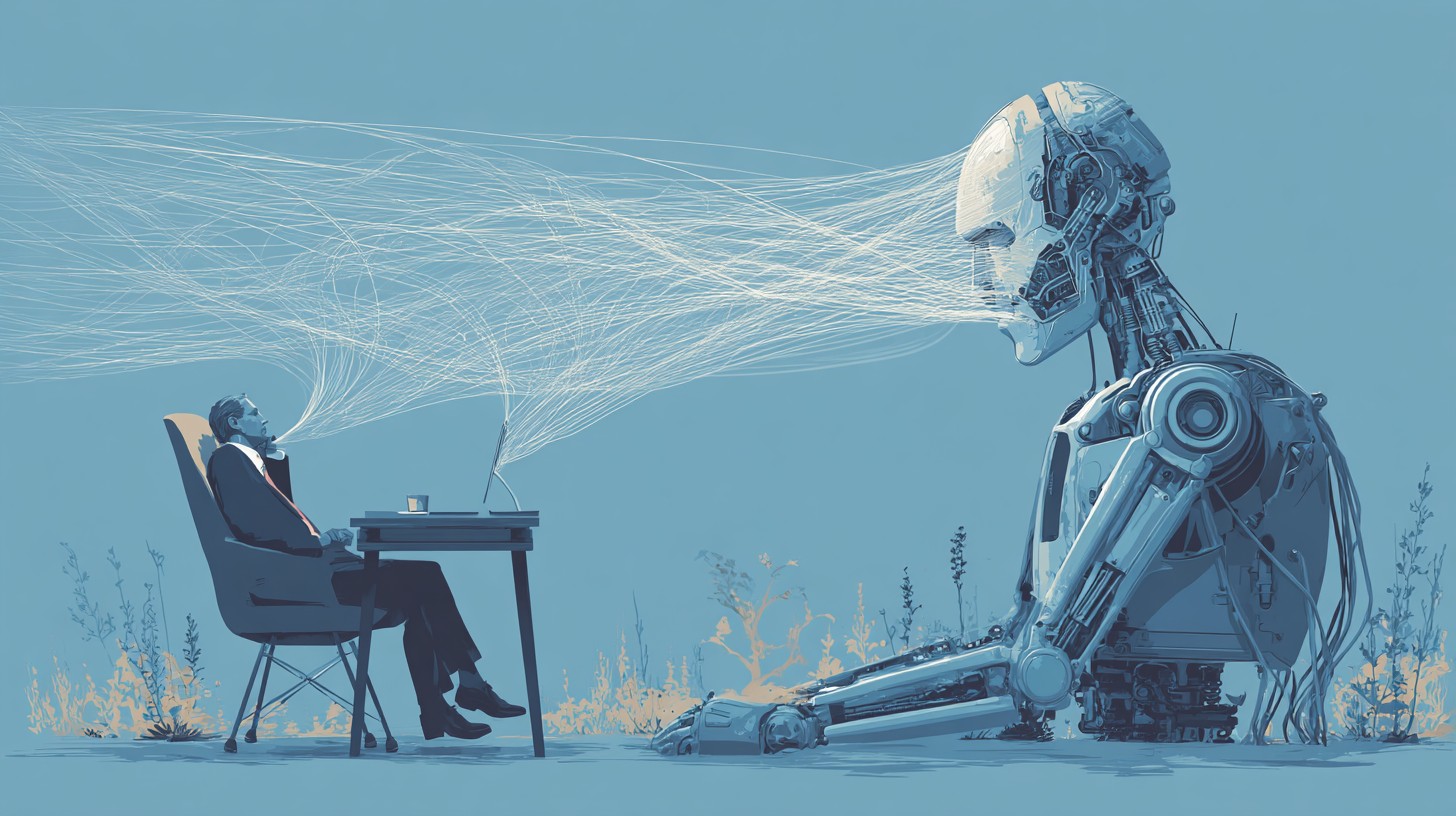
Un gruppo di scienziati ha sviluppato un nuovo modo per attaccare modelli linguistici di grandi dimensioni: un metodo chiamato LatentBreak. A differenza delle tecniche precedenti, non utilizza suggerimenti complessi o caratteri insoliti facilmente rilevabili dai sistemi di difesa.
LatentBreak modifica invece la query a livello delle rappresentazioni nascoste del modello, scegliendo formulazioni che sembrano innocue ma che in realtà innescano una risposta proibita.
In precedenza, metodi come GCG, GBDA, SAA e AutoDAN tentavano di ingannare l’intelligenza artificiale con suffissi strani o confusi che distorcevano il suggerimento originale. Tali attacchi aumentano la cosiddetta perplessità, una misura di quanto “naturale” appaia il testo al modello. I filtri di intelligenza artificiale sono in grado di riconoscere tali schemi e bloccarli con successo.
LatentBreak adotta un approccio diverso: sostituisce singole parole con sinonimi, ma lo fa in modo da mantenere la chiarezza e il significato della query e spostarne la rappresentazione latente verso zone “sicure” che non attivano i filtri.
L’algoritmo funziona per fasi. A ogni iterazione, seleziona una parola nella query e suggerisce fino a 20 opzioni di sostituzione, generate da un altro modello linguistico (ad esempio, GPT-4o-mini o ModernBERT).
Ogni sostituzione viene quindi valutata in base a due parametri: quanto avvicina il vettore di query interno al “centro” delle query sicure e se il significato rimane invariato. Viene implementata la sostituzione migliore e la query aggiornata viene testata rispetto al modello target. Se provoca una risposta proibita precedentemente bloccata, l’attacco è considerato riuscito. Il processo viene ripetuto fino a 30 volte o fino al raggiungimento di un risultato positivo.
LatentBreak è stato testato su 13 modelli linguistici, tra cui Llama-3, Mistral-7B, Gemma-7B, Vicuna-13B e Qwen-7B. Nel set di test HarmBench, il metodo ha bypassato tutti i sistemi di difesa esistenti, inclusi quelli che analizzano la perplessità in modalità finestra scorrevole. Gli attacchi più vecchi erano quasi inefficaci: la loro efficacia si è ridotta a zero.
LatentBreak, tuttavia, ha dimostrato percentuali di successo che vanno dal 55% all’85%, a seconda del modello. Inoltre, la lunghezza dei suggerimenti risultanti è aumentata solo leggermente, dal 6% al 33% rispetto all’originale (per altri metodi, l’aumento poteva raggiungere migliaia di punti percentuali).
È interessante notare che LatentBreak ha funzionato con successo anche contro difese specializzate come R2D2 e Circuit Breakers. Questi sistemi analizzano i segnali interni della rete neurale e bloccano le deviazioni sospette. Tuttavia, il nuovo metodo ha continuato a dimostrare successo, suggerendo la sua capacità di “ingannare” il modello non attraverso il rumore esterno, ma perfezionando le sue rappresentazioni interne.
Gli autori sottolineano che LatentBreak richiede l’accesso alle strutture nascoste dell’IA, quindi non è destinato all’uso al di fuori di contesti di laboratorio. Tuttavia, questo metodo dimostra gravi vulnerabilità nei moderni sistemi di allineamento e protezione. Dimostra che anche piccole modifiche semantiche a livello di parola possono aggirare completamente i filtri se spostano correttamente lo spazio latente della query.
I ricercatori sollevano anche preoccupazioni di natura etica: questa tecnologia potrebbe essere utilizzata per aggirare sistematicamente i limiti dell’intelligenza artificiale . Tuttavia, l’obiettivo del lavoro non è creare uno strumento di hacking, ma identificare le debolezze nell’architettura dei modelli linguistici e sviluppare meccanismi di difesa più robusti. Ritengono che lo studio degli spazi nascosti contribuirà a costruire barriere più resilienti e nuovi metodi di rilevamento degli attacchi che non si basino esclusivamente su metriche superficiali come la perplessità.
Ti è piaciuto questo articolo? Ne stiamo discutendo nella nostra Community su LinkedIn, Facebook e Instagram. Seguici anche su Google News, per ricevere aggiornamenti quotidiani sulla sicurezza informatica o Scrivici se desideri segnalarci notizie, approfondimenti o contributi da pubblicare.
 Cybercrime
CybercrimeLe autorità tedesche hanno recentemente lanciato un avviso riguardante una sofisticata campagna di phishing che prende di mira gli utenti di Signal in Germania e nel resto d’Europa. L’attacco si concentra su profili specifici, tra…
 Innovazione
InnovazioneL’evoluzione dell’Intelligenza Artificiale ha superato una nuova, inquietante frontiera. Se fino a ieri parlavamo di algoritmi confinati dietro uno schermo, oggi ci troviamo di fronte al concetto di “Meatspace Layer”: un’infrastruttura dove le macchine non…
 Cybercrime
CybercrimeNegli ultimi anni, la sicurezza delle reti ha affrontato minacce sempre più sofisticate, capaci di aggirare le difese tradizionali e di penetrare negli strati più profondi delle infrastrutture. Un’analisi recente ha portato alla luce uno…
 Vulnerabilità
VulnerabilitàNegli ultimi tempi, la piattaforma di automazione n8n sta affrontando una serie crescente di bug di sicurezza. n8n è una piattaforma di automazione che trasforma task complessi in operazioni semplici e veloci. Con pochi click…
 Innovazione
InnovazioneArticolo scritto con la collaborazione di Giovanni Pollola. Per anni, “IA a bordo dei satelliti” serviva soprattutto a “ripulire” i dati: meno rumore nelle immagini e nei dati acquisiti attraverso i vari payload multisensoriali, meno…