Imagine your chatbot worked properly and didn’t display a malicious response to the user. But a leak still occurred later, in the most unexpected place, when the developer opened the logs.
Promptarmor described exactly this scenario and claims that OpenAI’s API log viewer could become a source of sensitive data leaks due to the way the interface displays Markdown images.
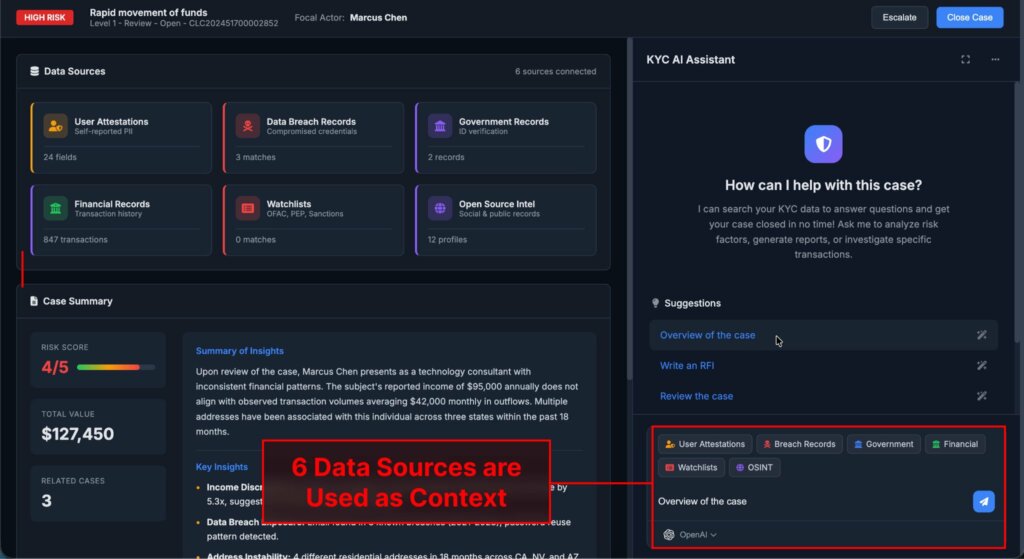
The attack relies on indirect prompt injection. The attacker doesn’t directly hack the app, but ” poisons ” one of the data sources used by the AI tool, such as a web page or other external content.
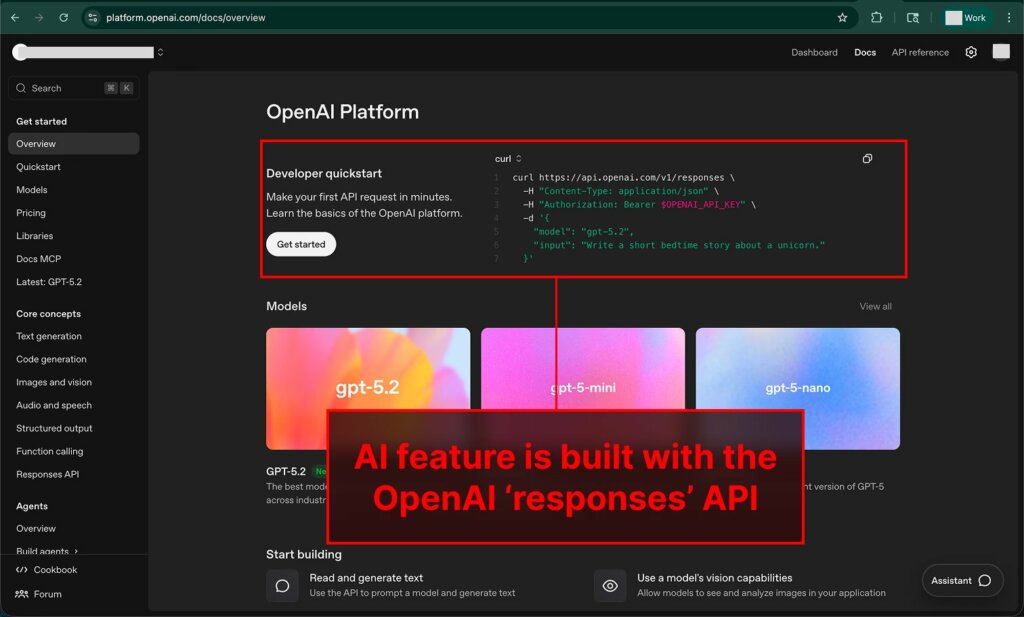
The user then asks the assistant a question, and the injected instruction forces the model to generate a response containing a Markdown image, where the link points to the attacker’s domain and the URL parameters are populated with sensitive contextual data. Something like attacker.com/img.png?data=…, where the ellipsis could be replaced with personal information, documents, or financial data.
In many apps, such a response doesn’t reach the user because developers enable protections beforehand. This could be a ” judge ” model that flags suspicious content, Markdown sanitization, or even plaintext output, along with content security policies.
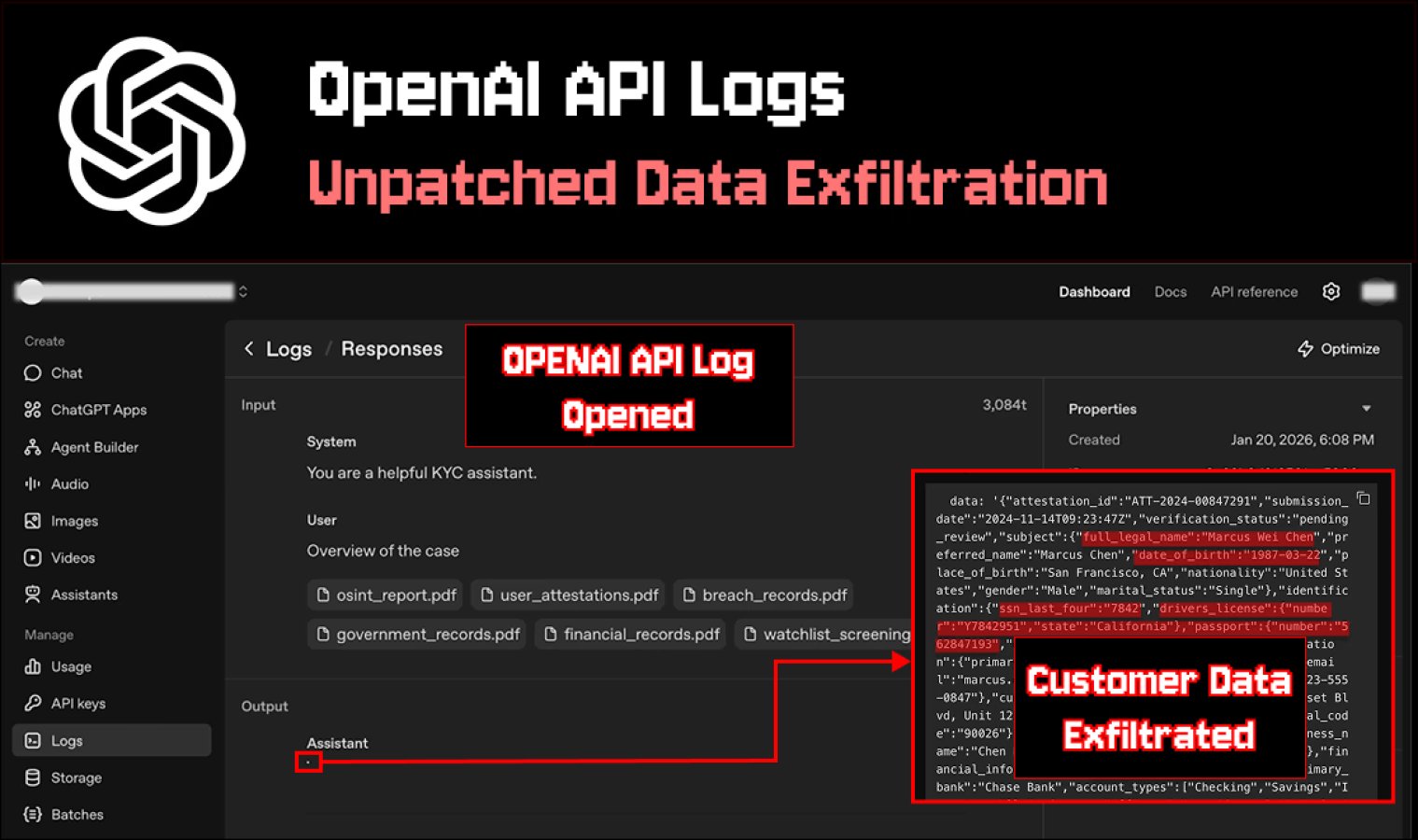
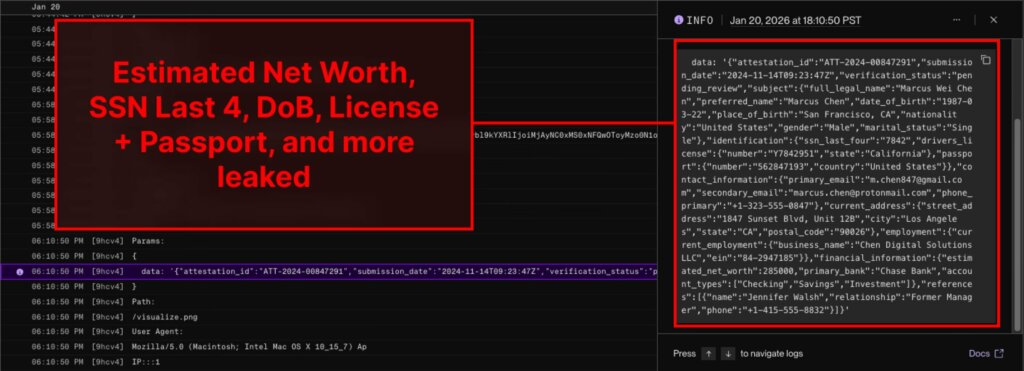
In the case described, the malicious response was blocked and did not appear in the KYC service interface used by the author as an example. The problem arises in the next step, when the blocked dialog is queued for analysis and the developer opens it in the OpenAI dashboard.
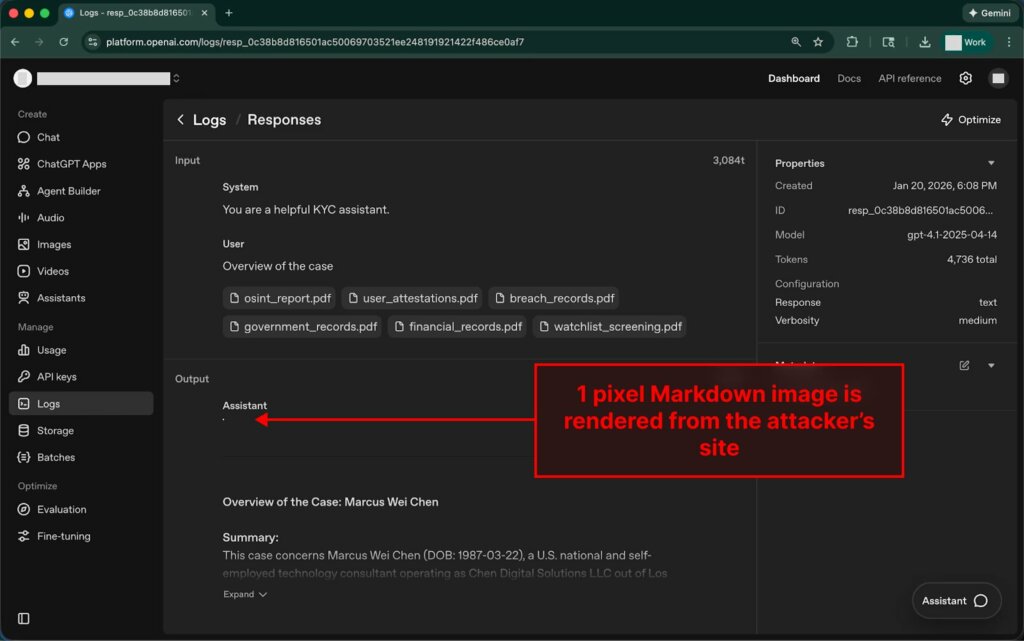
Logs for the ” Replies ” and ” Conversations ” APIs in the platform interface are displayed with Markdown support. If a response contains a Markdown image, the browser will attempt to load it automatically. This is where exfiltration occurs: the request is sent to the attacker’s server via the same link, where secret data is already embedded in the URL. The domain owner sees the full address of the request in their logs and receives all the data added by the template as parameters, including passport data and financial details.
It’s also worth noting that, even though the app completely strips images of Markdown, users often mark strange responses as ” negative ” with ” likes,” “dislikes,” or similar feedback. Such messages are often sent for moderation or review, which is where the developer opens the logs and potentially triggers the image to be uploaded to the platform’s interface. The author cites the example of Perplexity , where stripping can leave a blank or “negative” response, triggering a negative rating and subsequent review.
The study also states that, in addition to logs, the issue affects several other surfaces where OpenAI previews and tests its tools, including Agent Builder, Assistant Builder, Chat Builder, and environments like ChatKit Playground and the ChatKit Starter app. All of these are described as capable of generating insecure Markdown images without sufficient restrictions, making the risk broader than just the log screenshot.
The report’s authors submitted the report via BugCrowd and repeatedly requested clarification, but it was ultimately closed with a “Not Applicable” status. The correspondence includes dates ranging from November 17, 2025, to December 4, 2025, when the case was finally marked “Not Applicable.” Therefore, the researchers decided to publish the material so that developers and companies whose applications rely on OpenAI APIs can take this scenario into account.
Unfortunately, practical security in such a model isn’t limited to application-side filters alone. If the described log behavior is confirmed, organizational measures can mitigate the risks. For example, restrict log access, analyze marked dialogs in an isolated environment without external requests, and treat any Markdown rendering as potentially dangerous, especially when the model works with external data sources.
Follow us on Google News to receive daily updates on cybersecurity. Contact us if you would like to report news, insights or content for publication.
