
Una vulnerabilità denominata MadeYouReset è stata scoperta in diverse implementazioni HTTP/2. Questa vulnerabilità può essere sfruttata per lanciare potenti attacchi DDoS.
I ricercatori di Imperva , Deepness Lab e dell’Università di Tel Aviv scrivono che la vulnerabilità ha ricevuto l’identificatore primario CVE-2025-8671. Tuttavia, il bug interessa prodotti di vari fornitori, molti dei quali hanno già rilasciato i propri CVE e bollettini di sicurezza: Apache Tomcat (CVE-2025-48989), F5 BIG-IP (CVE-2025-54500), Netty (CVE-2025-55163), Vert.x e Varnish.
È stato inoltre segnalato che le soluzioni di Mozilla, Wind River, Zephyr Project, Google, IBM e Microsoft sono vulnerabili, il che potrebbe esporre i sistemi vulnerabili a rischi in un modo o nell’altro.
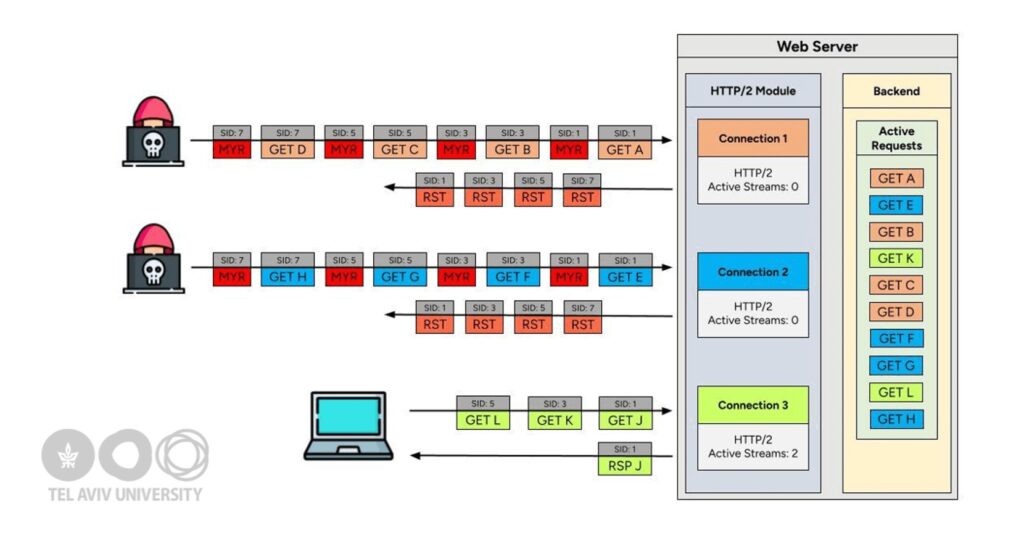
“MadeYouReset aggira il limite standard del server di 100 richieste HTTP/2 simultanee per connessione TCP client“, spiegano gli esperti. “Questo limite è progettato per proteggere dagli attacchi DoS limitando il numero di richieste simultanee che un client può inviare. Con MadeYouReset, un aggressore può inviare migliaia di richieste, creando condizioni DoS per utenti legittimi e, in alcune implementazioni, questo può portare a crash e condizioni di memoria insufficiente.”
La vulnerabilità MadeYouReset è simile ai problemi Rapid Reset e Continuation Flood , che sono stati sfruttati in potenti attacchi DDoS zero-day.
Come questi due attacchi, che sfruttano i frame RST_STREAM e CONTINUATION nel protocollo HTTP/2, MadeYouReset si basa su Rapid Reset e aggira la protezione che limita il numero di flussi che un client può annullare tramite RST_STREAM.
L’attacco sfrutta il fatto che il frame RST_STREAM viene utilizzato sia per la cancellazione avviata dal client che per la segnalazione degli errori di flusso. MadeYouReset funziona inviando frame appositamente creati che causano violazioni impreviste del protocollo, costringendo il server a reimpostare il flusso tramite RST_STREAM.
“Affinché MadeYouReset si attivi, un flusso deve iniziare con una richiesta valida su cui il server inizia a lavorare, e poi generare un errore in modo che il server ricorra a RST_STREAM mentre il backend continua a elaborare la risposta“, scrivono i ricercatori. “Creando determinati frame di controllo non validi o interrompendo il protocollo al momento giusto, possiamo forzare il server a utilizzare RST_STREAM su un flusso che conteneva già una richiesta valida.”
Inoltre, Imperva sottolinea che MadeYouReset è mescolato al traffico normale, rendendo tali attacchi difficili da rilevare.
Gli esperti suggeriscono una serie di misure che dovrebbero contribuire a proteggere da MadeYouReset, tra cui l’utilizzo di una convalida del protocollo più rigorosa, l’implementazione di un monitoraggio più rigoroso dello stato del flusso per rifiutare le transizioni non valide, l’implementazione di un controllo della velocità a livello di connessione e l’implementazione di sistemi di rilevamento delle anomalie e di monitoraggio comportamentale.
Ti è piaciuto questo articolo? Ne stiamo discutendo nella nostra Community su LinkedIn, Facebook e Instagram. Seguici anche su Google News, per ricevere aggiornamenti quotidiani sulla sicurezza informatica o Scrivici se desideri segnalarci notizie, approfondimenti o contributi da pubblicare.
 Innovazione
InnovazioneL’evoluzione dell’Intelligenza Artificiale ha superato una nuova, inquietante frontiera. Se fino a ieri parlavamo di algoritmi confinati dietro uno schermo, oggi ci troviamo di fronte al concetto di “Meatspace Layer”: un’infrastruttura dove le macchine non…
 Cybercrime
CybercrimeNegli ultimi anni, la sicurezza delle reti ha affrontato minacce sempre più sofisticate, capaci di aggirare le difese tradizionali e di penetrare negli strati più profondi delle infrastrutture. Un’analisi recente ha portato alla luce uno…
 Vulnerabilità
VulnerabilitàNegli ultimi tempi, la piattaforma di automazione n8n sta affrontando una serie crescente di bug di sicurezza. n8n è una piattaforma di automazione che trasforma task complessi in operazioni semplici e veloci. Con pochi click…
 Innovazione
InnovazioneArticolo scritto con la collaborazione di Giovanni Pollola. Per anni, “IA a bordo dei satelliti” serviva soprattutto a “ripulire” i dati: meno rumore nelle immagini e nei dati acquisiti attraverso i vari payload multisensoriali, meno…
 Cyber Italia
Cyber ItaliaNegli ultimi giorni è stato segnalato un preoccupante aumento di truffe diffuse tramite WhatsApp dal CERT-AGID. I messaggi arrivano apparentemente da contatti conosciuti e richiedono urgentemente denaro, spesso per emergenze come spese mediche improvvise. La…