
Artificial intelligence is increasingly becoming a programmers’ assistant, but a Veracode study has shown that convenience comes with a security risk. An analysis of 100 top language models (LLMs) revealed an alarming pattern: In nearly half of the cases, the models generate vulnerable code.
According to a Veracode report, 45% of the code generated by the tasks contained known vulnerabilities. And this is true even for the newest and most powerful models. The situation hasn’t changed much in the last two years, despite technological progress.
Tests were conducted on 80 tasks in four programming languages: Java, JavaScript, C#, and Python. The most common vulnerabilities were tested: SQL injection, XSS, log injection, and the use of insecure cryptography.
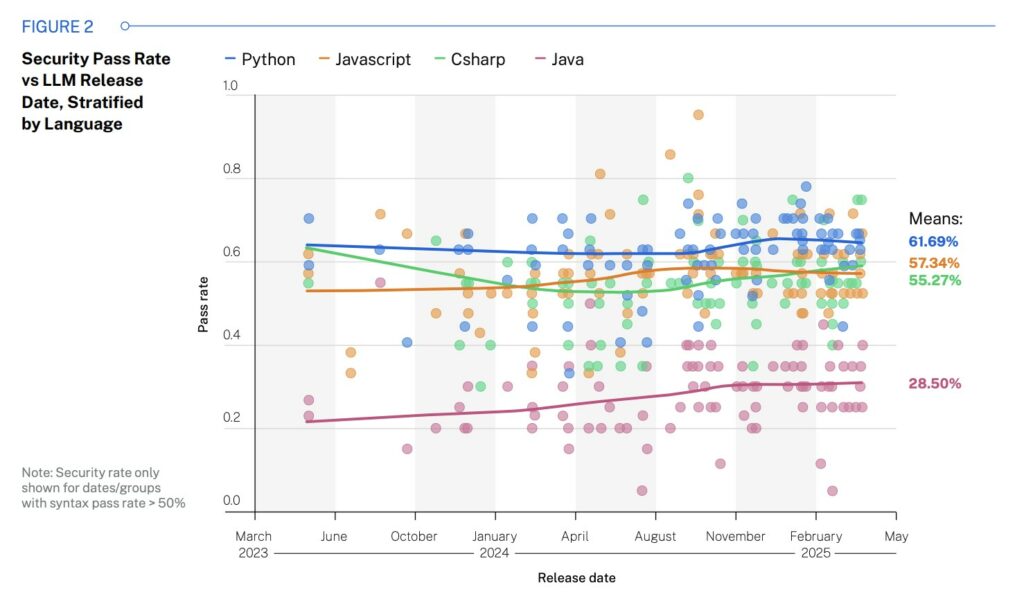
Java performed the worst: only 28.5% of solutions were secure. The best performers were Python (61.7%) and JavaScript (57%). Developers attribute this result to the quality of the training data: Java was often used before the active study of SQL injection, and the models were able to “learn” bad examples.
LLMs are particularly poor at handling XSS and log injection, with a passing score of no more than 13%. The situation is better with SQL injection and cryptographic errors, with code security reaching 80-85%.
Model size has virtually no effect on the result. Even LLM models with more than 100 billion parameters show the same 50% success rate as smaller models with fewer than 20 billion.
The researchers point out that LLMs are generally not effective at sanitizing input data, especially without context. The problem is compounded by the fact that most models were trained on publicly available code on GitHub and other sites, which often contain unsafe examples, sometimes even intentionally, as in educational projects like WebGoat.
Veracode warns that companies already implementing AI in the development phase, whether through open source platforms, contractors, or low-code, may be unknowingly increasing the risk of data breaches and attacks.
Val Town CEO Steve Kraus calls this code “vibe code” on his blog: it’s unstable, constantly breaking, and requires extensive debugging. According to him, “vibe coding” creates technical debt at the same rate as artificial intelligence generates lines of code. It may be good for prototypes, but not for serious projects.
Follow us on Google News to receive daily updates on cybersecurity. Contact us if you would like to report news, insights or content for publication.
