
Il termine “hacktivismo” è la combinazione tra i termini inglesi “hacking” e “hacktivism” ed è stato coniato per descrivere l’uso dell’hacking informatico per fini politici o sociali.
Si tratta di un fenomeno complesso che coinvolge gruppi hacker e attivisti, spesso operanti a livello internazionale, che utilizzano le tecniche di hacking per promuovere idee o protestare contro governi, istituzioni o multinazionali.
Le motivazioni degli hacktivisti possono essere molteplici, ma quasi sempre legate ad ideali politici, sociali o etici, o a specifici eventi o sempre di più a situazioni di crisi nazionale.
In questo articolo andremo ad esplorare cos’è l’hacktivismo cibernetico, passando dalla sua storia e dalla dichiarazione di hacktivismo dei “Cult of the dead Cow”, per poi arrivare alle tecniche, alle conseguenze e alle sue evoluzioni per poi parlare delle “Milizie cyber”.

L’hacktivismo cibernetico si distingue dall’hacking tradizionale per le finalità politiche o sociali che lo motivano. In genere, gli hacktivisti cercano di utilizzare le loro abilità informatiche per promuovere una causa o per protestare contro una decisione politica o economica ritenuta ingiusta. In tal modo, gli hacktivisti si pongono come oppositori dell’ordine costituito e cercano di influenzare la società in modo radicale.
L’hacktivismo cibernetico è stato protagonista di molte azioni di rilievo negli ultimi anni. Tra le più note ci sono le attività del gruppo Anonymous, nato negli Stati Uniti nel 2003 e diventato famoso per le sue operazioni contro governi e organizzazioni che riteneva colpevoli di abusi o corruzione. Anonymous è stato protagonista di numerose azioni di protesta, tra cui il supporto alla Primavera Araba e la denuncia degli abusi sui diritti umani in diversi Paesi del mondo.
In sintesi, l’hacktivismo cibernetico rappresenta una forma di protesta e di attivismo che utilizza le tecniche di hacking per ottenere visibilità e promuovere un’agenda politica o sociale. Si tratta di un fenomeno complesso e variegato, che coinvolge gruppi di hacker e attivisti in tutto il mondo. Nelle prossime sezioni del nostro articolo, analizzeremo la storia e l’evoluzione dell’hacktivismo cibernetico, le sue motivazioni, le forme di protesta utilizzate e le conseguenze sulle società e le istituzioni.
L’hacktivismo cibernetico ha una storia lunga e complessa che risale agli anni ’80, quando i primi gruppi di hacker cominciarono ad utilizzare le tecniche di hacking per scopi politici e sociali.
Uno dei primi gruppi ad utilizzare le tecniche di hacking per fini politici fu il Chaos Computer Club (CCC), fondato in Germania nel 1981. Il CCC si definiva come un gruppo di hacker “etici”, che cercava di utilizzare le proprie abilità informatiche per promuovere la libertà di espressione e il diritto alla privacy. Il CCC ha organizzato numerose conferenze e manifestazioni per promuovere i propri ideali e ha contribuito alla diffusione della cultura hacker in tutto il mondo.
Successivamente nel 1984 venne redatta la “Dichiarazione di hacktivismo” da parte del gruppo hacker Cult of the dead Cow (CdC) che vedremo nel capitolo successivo.
Negli anni ’90, l’hacktivismo cibernetico ha acquisito maggiore visibilità grazie alle azioni del gruppo Electronic Disturbance Theater (EDT), fondato negli Stati Uniti nel 1998. L’EDT si è distinto per le sue “performance” di hacking, che consistevano nell’organizzare attacchi DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) contro siti web di organizzazioni governative o aziendali ritenute responsabili di abusi o ingiustizie.
Nel corso degli anni 2000, l’hacktivismo cibernetico ha continuato a evolversi e a diffondersi in tutto il mondo. Uno dei gruppi più noti è Anonymous, nato negli Stati Uniti nel 2003 e diventato famoso per le sue azioni di protesta contro governi e organizzazioni ritenute colpevoli di abusi o corruzione. Anonymous ha utilizzato le tecniche di hacking per promuovere una vasta gamma di cause, tra cui la libertà di espressione, la lotta alla corruzione e il diritto alla privacy.
In sintesi, l’hacktivismo cibernetico ha radici profonde nella cultura hacker degli anni ’80 e ’90, quando i primi gruppi cominciarono ad utilizzare le tecniche di hacking per fini politici e sociali. Nel corso degli anni, l’hacktivismo cibernetico ha continuato a evolversi e a diffondersi in tutto il mondo, diventando un fenomeno complesso e variegato che coinvolge gruppi di hacker e attivisti in tutto il mondo.
La Dichiarazione di Hacktivismo dei CDC (Cult of the Dead Cow) è un documento storico dell’hacktivismo cibernetico che ha avuto un impatto significativo sulla cultura hacker e sull’attivismo digitale. Il CDC è stato fondato negli Stati Uniti nel 1984 ed è stato uno dei primi gruppi di hacker a definirsi come “etici” e a sostenere l’uso delle proprie abilità informatiche per fini sociali e politici.
La Dichiarazione di Hacktivismo dei CDC è stata pubblicata nel 1996 ed è stata una delle prime dichiarazioni ufficiali a sostenere l’hacktivismo come forma legittima di protesta politica. Nel documento, i membri del CDC affermavano che “l’hacktivismo è una forma di espressione politica che utilizza le abilità informatiche per comunicare messaggi di protesta e di resistenza”.
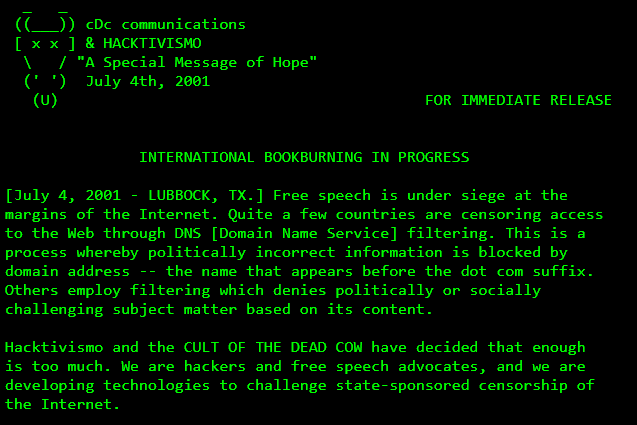
La Dichiarazione di Hacktivismo dei CDC ha avuto un impatto significativo sulla cultura hacker e sull’attivismo digitale. Ha contribuito a legittimare l’uso delle tecniche di hacking per fini sociali e politici e ha ispirato molti altri gruppi di hacktivisti in tutto il mondo.
È importante notare che l’hacktivismo cibernetico può essere una pratica complessa e controversa. Mentre alcuni lo vedono come una forma legittima di protesta politica, altri lo considerano una forma di criminalità informatica. In ogni caso, la Dichiarazione di Hacktivismo dei CDC ha contribuito a creare un dibattito sul ruolo dell’hacktivismo nella società e sulle sue implicazioni etiche e legali.
L’hacktivismo cibernetico è spesso motivato da ideali politici, sociali o etici. Gli hacktivisti possono utilizzare le loro abilità informatiche per promuovere la libertà di espressione, la lotta alla corruzione, la difesa dei diritti umani e la protezione della privacy.
In alcuni casi, gli hacktivisti possono essere motivati anche da cause più specifiche. Ad esempio, durante la guerra tra Ucraina e Russia, il gruppo di hacker ucraini noto come “CyberBerkut” ha organizzato numerosi attacchi informatici contro siti web russi, in segno di protesta contro l’annessione della Crimea da parte della Russia e il sostegno dei separatisti ucraini da parte del governo russo.
Stessa cosa ha fatto la Russia utilizzano di collettivi hacker quali “Killnet” e “Noname057(16)“, che hanno attaccato ripetutamente obiettivi occidentali che supportavano l’Ucraina dove molti di questi attacchi hanno colpito anche l’Italia.
Tuttavia, va sottolineato che l’hacktivismo cibernetico può anche essere utilizzato per scopi illeciti e dannosi. Gli attacchi informatici possono causare danni economici e compromettere la sicurezza delle persone e delle organizzazioni coinvolte. Pertanto, è importante distinguere tra hacktivismo “etico” e hacktivismo illegale o criminale.

Il gruppo hacktivista Anonymous è uno dei più noti e influenti nel mondo dell’hacktivismo cibernetico. Il gruppo è stato fondato nel 2003 da un gruppo di utenti del forum 4chan, con l’obiettivo di protestare contro la Chiesa di Scientology e la sua politica di censura su internet. Da allora, il gruppo ha portato avanti numerose azioni di protesta e attacchi informatici contro organizzazioni e governi in tutto il mondo.
Anonymous è noto per l’utilizzo di una maschera raffigurante il personaggio di Guy Fawkes, tratto dal fumetto e film “V per Vendetta”, come simbolo della sua attività. La maschera rappresenta l’anonimato, uno dei principi fondamentali del gruppo.
Tra le azioni di Anonymous, si possono citare l’operazione Payback, in cui il gruppo ha attaccato i siti web di diverse organizzazioni, tra cui la RIAA e la MPAA, in protesta contro le restrizioni sulle attività di file sharing, e l’operazione Chanology, contro la Chiesa di Scientology.
Ma non tutte le azioni di Anonymous sono state mirate contro organizzazioni o governi. Il gruppo ha anche svolto attività di supporto, come quando ha lanciato l’operazione Safe Winter, per aiutare i senzatetto durante l’inverno.
Una delle caratteristiche più interessanti di Anonymous è la sua struttura decentralizzata e leaderless. Il gruppo non ha un leader o una gerarchia formale, ma si organizza attraverso una serie di canali su internet, come IRC e i social media. Questa struttura rende difficile per le autorità individuare e fermare gli attivisti di Anonymous.
Inoltre, il gruppo è noto per l’utilizzo di tecniche di hacking sofisticate e per la sua capacità di penetrare nei sistemi informatici di organizzazioni e governi. Anonymous ha anche sviluppato un’ampia gamma di strumenti di hacking, come LOIC (Low Orbit Ion Cannon), un software utilizzato per effettuare attacchi DDoS.
In sintesi, Anonymous rappresenta uno dei gruppi di hacktivisti più noti e influenti al mondo, noto per le sue azioni di protesta e attacchi informatici. La struttura decentralizzata e l’utilizzo di tecniche di hacking sofisticate lo rendono un avversario difficile da individuare e fermare per le autorità.
L’hacktivismo cibernetico può assumere molte forme diverse. Di seguito ne riportiamo alcune tra le più comuni:
In conclusione, l’hacktivismo cibernetico è un fenomeno che assume forme diverse a seconda delle cause, delle motivazioni e degli obiettivi degli hacktivisti coinvolti.

L’hacktivismo cibernetico è un fenomeno che si è diffuso in tutto il mondo, grazie alla diffusione di Internet e delle tecnologie informatiche. Gli hacktivisti sono presenti in tutti i paesi e agiscono su scala globale, utilizzando le reti informatiche per organizzare proteste e azioni di denuncia.
Negli ultimi anni, l’hacktivismo cibernetico è diventato sempre più diffuso in tutto il mondo, grazie alla facilità di accesso alle tecnologie informatiche e alla crescente consapevolezza dei cittadini sui temi della privacy e della libertà di espressione.
Alcuni dei gruppi hacktivisti più noti a livello internazionale includono Anonymous, LulzSec e AntiSec, che hanno attirato l’attenzione dei media per le loro azioni di protesta contro organizzazioni e istituzioni considerate responsabili di comportamenti immorali o illegali.
Anche in Italia l’hacktivismo cibernetico è presente da diversi anni. Tra i gruppi più noti vi sono hackitivisti.net e Anonymous Italia, che hanno organizzato diverse proteste online e offline contro le politiche governative e le restrizioni alla libertà di espressione.
L’hacktivismo cibernetico ha avuto un impatto significativo sulle società e sulle istituzioni in tutto il mondo. Da un lato, gli hacktivisti hanno utilizzato le loro abilità informatiche per protestare contro organizzazioni e istituzioni che considerano responsabili di comportamenti immorali o illegali. Dall’altro lato, queste attività hanno causato danni alle organizzazioni coinvolte e possono violare le leggi sulla privacy e sulla sicurezza informatica.
Uno dei principali effetti dell’hacktivismo cibernetico è la diffusione delle informazioni e delle idee. Grazie alle tecnologie informatiche, gli hacktivisti possono comunicare e coordinare le loro attività in modo anonimo, rapido ed efficace, raggiungendo un vasto pubblico in tutto il mondo. Ciò ha portato alla creazione di una nuova forma di attivismo, in grado di superare le barriere geografiche e linguistiche e di coinvolgere un pubblico sempre più ampio.
Tuttavia, l’hacktivismo cibernetico può anche avere effetti negativi sulle organizzazioni coinvolte. Le attività degli hacktivisti possono causare danni ai siti web e alle infrastrutture informatiche delle organizzazioni, causando perdite finanziarie e di reputazione. Inoltre, gli hacktivisti possono violare la privacy dei dipendenti e dei clienti delle organizzazioni, ottenendo informazioni sensibili che possono essere utilizzate per scopi illeciti.
L’hacktivismo cibernetico ha anche portato alla creazione di nuove norme e regolamenti sulla sicurezza informatica. Le organizzazioni sono ora tenute a proteggere i loro sistemi informatici da attacchi esterni e a prevenire la perdita di dati sensibili. Inoltre, le istituzioni governative hanno introdotto nuove leggi sulla sicurezza informatica e sul cybercrime, al fine di regolamentare l’attività degli hacktivisti e prevenire la diffusione di informazioni sensibili.

L’hacktivismo cibernetico si è evoluto nel corso degli anni, diventando sempre più sofisticato e organizzato. Inoltre, nuove sfide sono emerse con l’avvento di nuove tecnologie e la crescente consapevolezza delle autorità di contrastare l’hacktivismo.
Una delle principali evoluzioni dell’hacktivismo è stata l’adozione di nuove tecniche e strumenti. Ad esempio, il DDoS è diventato sempre più comune, ma anche tecniche di exploit più sofisticate sono state sviluppate. Inoltre, l’uso di reti anonime come Tor ha reso più difficile per le autorità tracciare gli hacker.
Un’altra tendenza recente è l’organizzazione dell’hacktivismo cibernetico in gruppi più strutturati e gerarchici. Questi gruppi hanno sviluppato una sorta di culto della personalità intorno ai loro membri più noti e sono stati in grado di attirare un gran numero di sostenitori.
Tuttavia, l’evoluzione dell’hacktivismo ha anche portato a nuove sfide. Ad esempio, molte nazioni hanno iniziato a sviluppare le loro capacità di hacking per utilizzarle come strumenti di guerra cibernetica. Ciò ha portato a una crescente militarizzazione dell’hacktivismo cibernetico, che può essere utilizzato come una sorta di arma per sostenere gli interessi nazionali.
Inoltre, le autorità stanno diventando sempre più abili nel tracciare gli hacker e identificarli. Ciò ha portato ad un aumento delle indagini e delle sentenze per i crimini informatici, con conseguente diminuzione del livello di anonimato e protezione per gli hacker.

L’hacktivismo cibernetico è un fenomeno complesso e in continua evoluzione, che ha dimostrato di poter avere un impatto significativo sulle società e le istituzioni. Come abbiamo visto, l’hacktivismo può assumere molte forme, dalle proteste pacifiche online alla diffusione di informazioni riservate o alla disinformazione, fino ad arrivare al sabotaggio o al cyber-attacco.
Come abbiamo riportato in precedenza, negli ultimi anni, abbiamo assistito alla nascita delle “Milizie cyber”, gruppi di hacktivisti organizzati e altamente specializzati, che possono rappresentare una minaccia seria per la sicurezza informatica delle istituzioni e delle imprese. Questi gruppi possono avere obiettivi diversi, da quelli politici a quelli economici o sociali.
Inoltre, la recente guerra tra Ucraina e Russia ha visto un’escalation di attacchi informatici da entrambe le parti, che hanno coinvolto anche gruppi di hacktivisti. Questi fatti dimostrano che l’hacktivismo è utilizzato anche per fini nazionali, oltre che per scopi politici o sociali.
Nonostante gli effetti positivi dell’hacktivismo cibernetico, come la diffusione di informazioni o la denuncia di ingiustizie, non dobbiamo sottovalutare i rischi che esso comporta, come la violazione della privacy o la compromissione della sicurezza informatica. È importante che i governi, le istituzioni e le imprese lavorino per prevenire e proteggersi da questi rischi, senza però compromettere la libertà di espressione e la trasparenza.
In conclusione, l’hacktivismo cibernetico rimane un fenomeno in continua evoluzione, che richiede una costante attenzione e adattamento da parte di tutti gli attori coinvolti. Il futuro dell’hacktivismo dipenderà dalle scelte che la società e le istituzioni faranno nei prossimi anni, ma è certo che esso continuerà ad avere un ruolo importante nella società digitale.
Ti è piaciuto questo articolo? Ne stiamo discutendo nella nostra Community su LinkedIn, Facebook e Instagram. Seguici anche su Google News, per ricevere aggiornamenti quotidiani sulla sicurezza informatica o Scrivici se desideri segnalarci notizie, approfondimenti o contributi da pubblicare.
 Cybercrime
CybercrimeLe autorità tedesche hanno recentemente lanciato un avviso riguardante una sofisticata campagna di phishing che prende di mira gli utenti di Signal in Germania e nel resto d’Europa. L’attacco si concentra su profili specifici, tra…
 Innovazione
InnovazioneL’evoluzione dell’Intelligenza Artificiale ha superato una nuova, inquietante frontiera. Se fino a ieri parlavamo di algoritmi confinati dietro uno schermo, oggi ci troviamo di fronte al concetto di “Meatspace Layer”: un’infrastruttura dove le macchine non…
 Cybercrime
CybercrimeNegli ultimi anni, la sicurezza delle reti ha affrontato minacce sempre più sofisticate, capaci di aggirare le difese tradizionali e di penetrare negli strati più profondi delle infrastrutture. Un’analisi recente ha portato alla luce uno…
 Vulnerabilità
VulnerabilitàNegli ultimi tempi, la piattaforma di automazione n8n sta affrontando una serie crescente di bug di sicurezza. n8n è una piattaforma di automazione che trasforma task complessi in operazioni semplici e veloci. Con pochi click…
 Innovazione
InnovazioneArticolo scritto con la collaborazione di Giovanni Pollola. Per anni, “IA a bordo dei satelliti” serviva soprattutto a “ripulire” i dati: meno rumore nelle immagini e nei dati acquisiti attraverso i vari payload multisensoriali, meno…