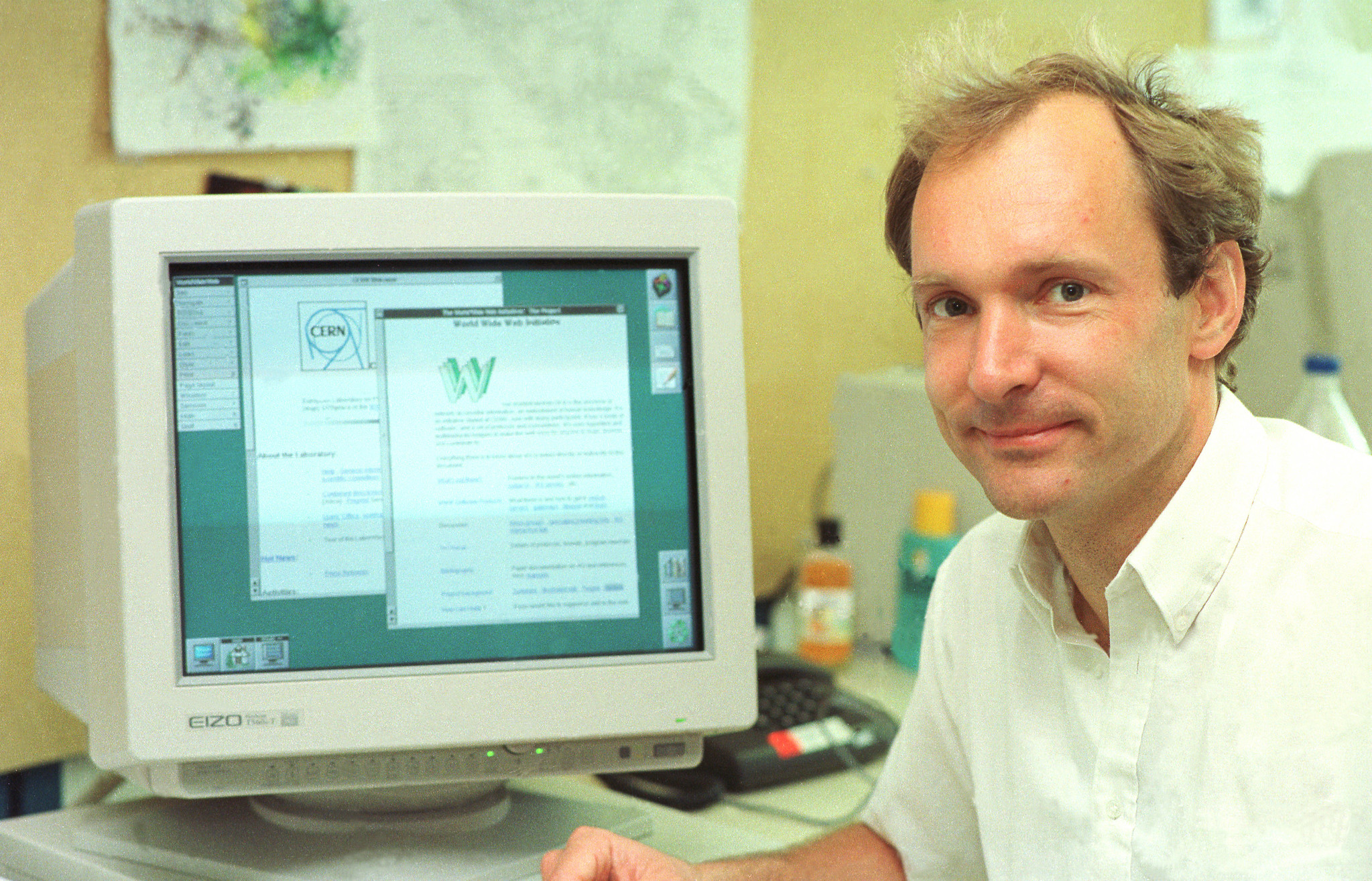

We all use the internet every day, at all hours, our smartphone has become an active prosthesis of our body, but have we ever wondered who invented the World Wide Web?
Today we talk about Timothy Berners-Lee, the British computer scientist, who received the prestigious Turing Award in 2016 for the invention of the World Wide Web together with Robert Caigliu.
But let’s proceed in order. In 1989, at CERN in Geneva, the most important European physics laboratory, Berners-Lee was struck by how some Italian colleagues were using a telephone line to transmit information from one floor of the CERN building to another, displaying information via video.
On March 12, 1989, Tim and his colleague Robert presented a proposal to their supervisor for efficiency improvements through software that would allow the sharing of scientific documentation among the institute’s researchers, effectively increasing collaboration.
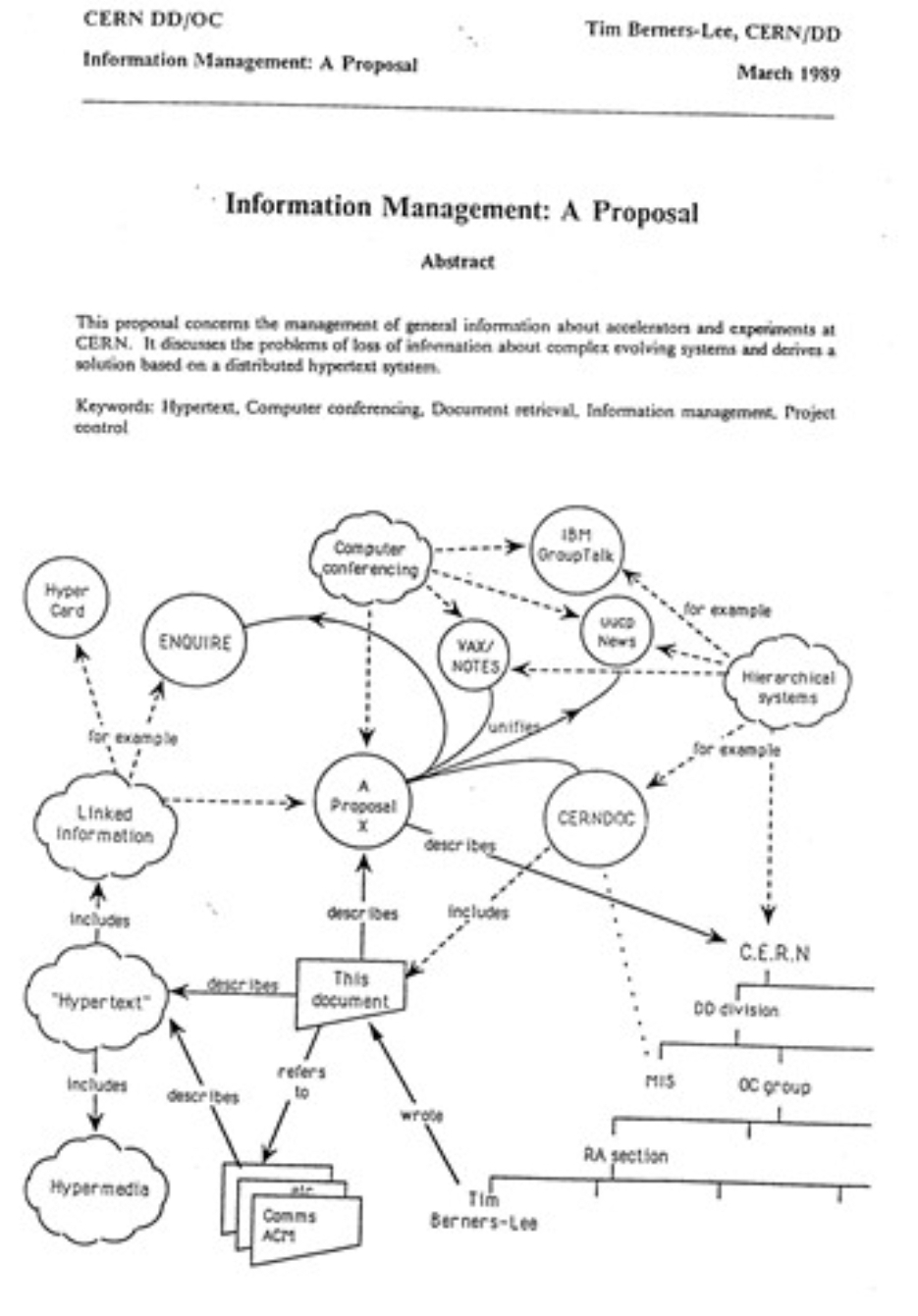
This work was presented by the two, but initially evaluated as “vague but interesting”.
The two began developing the software that effectively began defining the standards and protocols for exchanging documents over computer networks: the HTML language, which allows for the production of documents, and the HTTP network protocol, which allows for their transport.
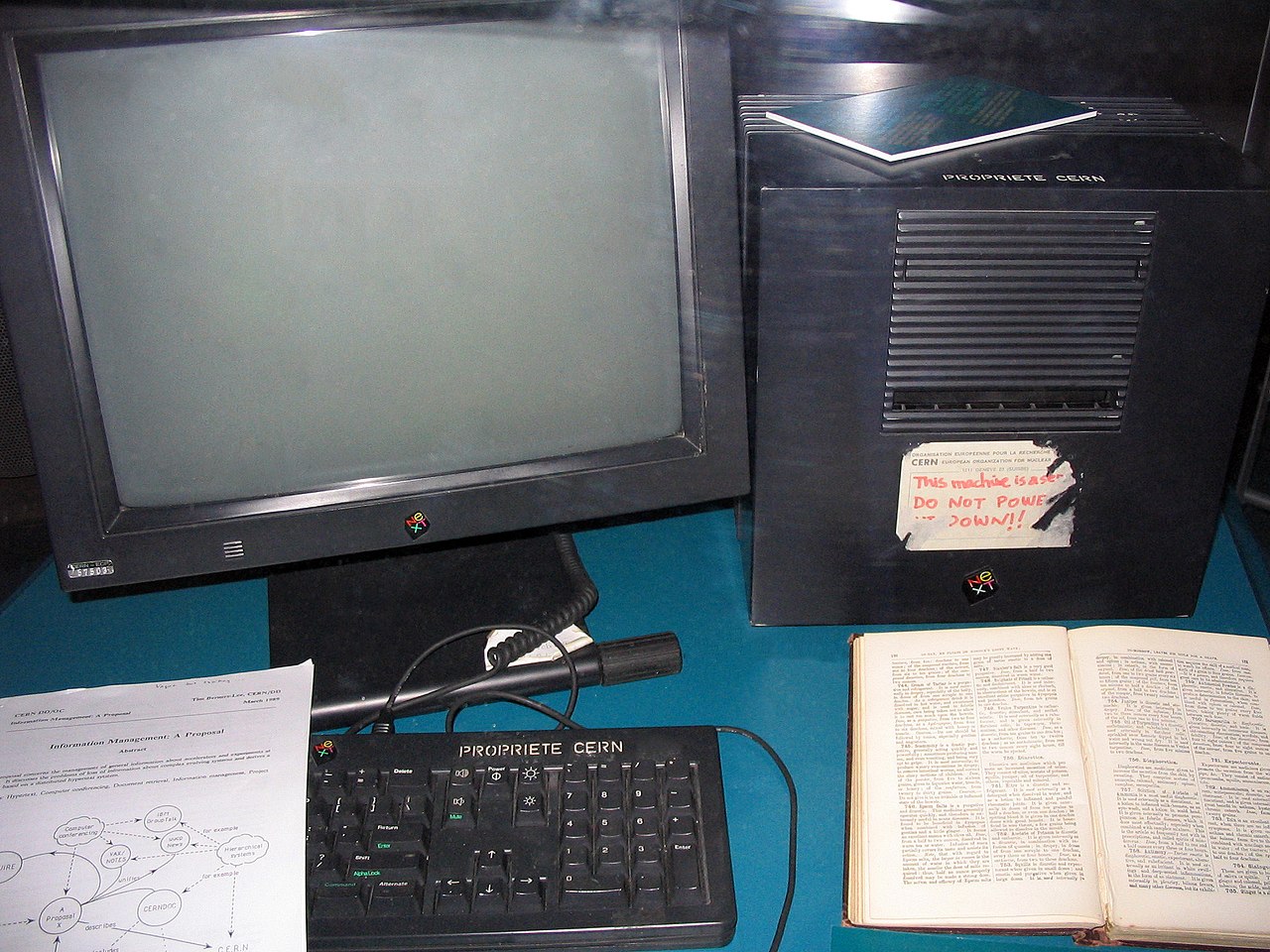

In fact, on December 20, 1990 , the first website in history reporting on the World Wide Web project appeared. This site was only visible on the CERN network, and to view it, the first hypertext browser was also created.
On December 6, 1991, Tim began announcing the existence of the WWW project and the availability of the software on various newsgroups.
Consider that only after 17 days, the first visit to the page took place, while the first user external to the research center reached the website on August 23 of the following year.
From then on, the web became unstoppable and became what we all know today, with all the good and bad things associated with it, and Berners Lee soon realized this.
But Berners Lee, speaking at a conference in Rome in 2011, said:
“We need to start talking about the right to access the internet and the right not to be spied on. The internet must remain free, open, and neutral.”
This is not the first time that Tim has testified about the poor social state of the Internet, saying that what is the Internet today is not the essence of the project that was born at CERN, adding:
“The Internet can become a positive tool again”
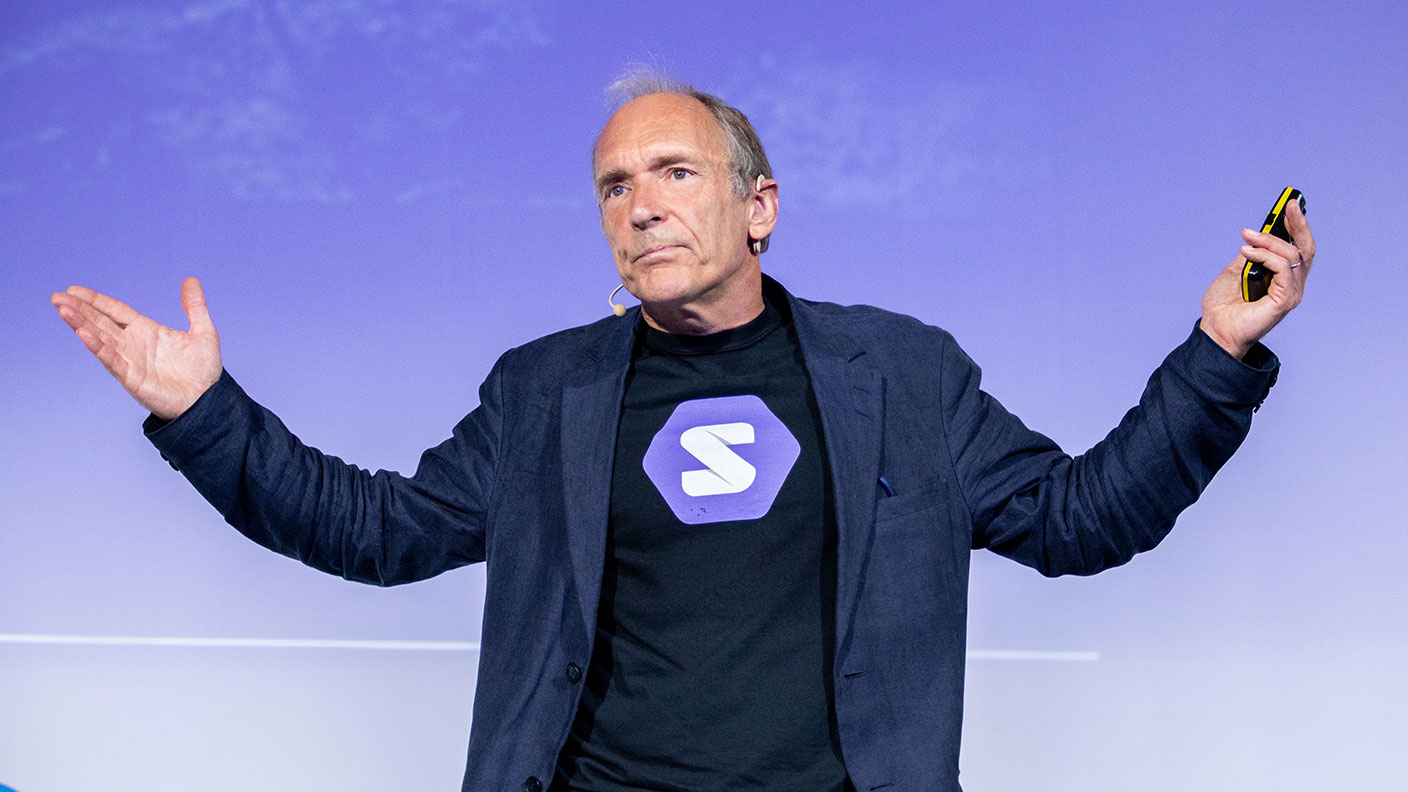

Here is a response from Berners Lee himself , who feels somewhat responsible for his creation, with the launch of the “Solid” project, a “decentralized” internet that can guarantee data protection, taking power away from the digital giants.
Many are the honors that have celebrated his prodigious inventions, including the Marconi Prize and the Millennium Technology Award and finally in 2016 the prestigious Turing Award, which we mentioned at the beginning of the document.
The WWW is considered one of the most influential computer innovations in history, used by billions of people every day as the primary tool for communication, information, commerce, and numerous other activities.
Follow us on Google News to receive daily updates on cybersecurity. Contact us if you would like to report news, insights or content for publication.
