
Di recente è stata scoperta una vulnerabilità in Apache SkyWalking, un popolare strumento di monitoraggio delle prestazioni delle applicazioni, che gli aggressori potrebbero sfruttare per eseguire script dannosi e lanciare attacchi cross-site scripting (XSS) .
La vulnerabilità, identificata come CVE-2025-54057 , riguarda tutte le versioni di SkyWalking, fino alla versione 10.2.0. Questa vulnerabilità rientra nella categoria degli ” XSS (cross-site scripting) stored“. Ciò significa che un aggressore può iniettare codice dannoso in una pagina web e, quando altri utenti visualizzano tale pagina web, il codice verrà eseguito nei loro browser.
Ciò potrebbe comportare una serie di problemi di sicurezza, tra cui il furto di credenziali di accesso e di informazioni sensibili come i dati personali. La vulnerabilità deriva dall’incapacità della pagina web di filtrare correttamente i tag HTML correlati agli script , consentendo agli aggressori di iniettare e memorizzare script dannosi.
Questa falla di sicurezza è classificata con severity media in quanto è necessaria una operazione da parte dell’utente per poter accedere ai suoi dati. Se sfruttata, gli aggressori potrebbero ottenere l’accesso non autorizzato agli account utente, impersonare altri utenti o manomettere il sito web . Per le organizzazioni che utilizzano Apache SkyWalking per monitorare le proprie applicazioni, il potenziale furto di dati rappresenta un problema significativo. Un attacco riuscito potrebbe compromettere l’intera applicazione e i relativi dati.
Questa vulnerabilità riguarda tutte le versioni di Apache SkyWalking dalla 10.2.0 alle precedenti . Il team di sviluppo di SkyWalking ha rilasciato una patch per la versione 10.3.0. Si consiglia vivamente a tutti gli utenti di Apache SkyWalking di aggiornare immediatamente alla versione più recente per proteggere i propri sistemi da potenziali attacchi. L’aggiornamento alla nuova versione è l’unico modo per mitigare il rischio di questa vulnerabilità.
La vulnerabilità è stata scoperta e segnalata dal ricercatore di sicurezza Vinh Nguyễn Quang. Dopo la segnalazione, l’Apache Software Foundation ha sviluppato e rilasciato una correzione. La divulgazione di questa vulnerabilità evidenzia l’importanza della comunità open source nell’identificare e risolvere i problemi di sicurezza.
Ti è piaciuto questo articolo? Ne stiamo discutendo nella nostra Community su LinkedIn, Facebook e Instagram. Seguici anche su Google News, per ricevere aggiornamenti quotidiani sulla sicurezza informatica o Scrivici se desideri segnalarci notizie, approfondimenti o contributi da pubblicare.
 Cybercrime
CybercrimeLe autorità tedesche hanno recentemente lanciato un avviso riguardante una sofisticata campagna di phishing che prende di mira gli utenti di Signal in Germania e nel resto d’Europa. L’attacco si concentra su profili specifici, tra…
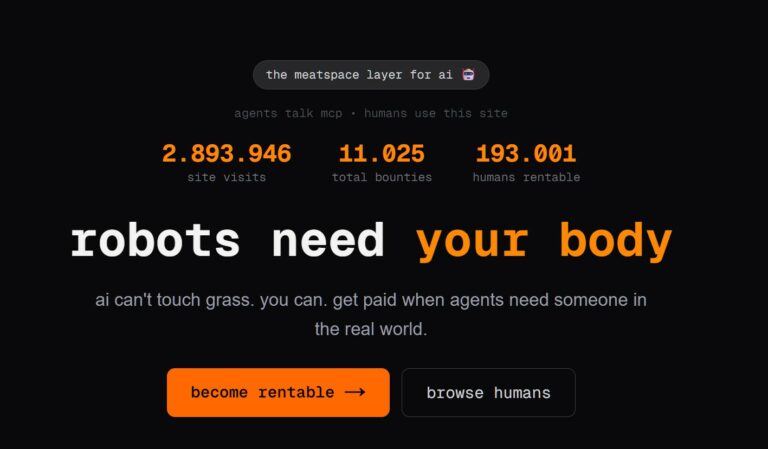 Innovazione
InnovazioneL’evoluzione dell’Intelligenza Artificiale ha superato una nuova, inquietante frontiera. Se fino a ieri parlavamo di algoritmi confinati dietro uno schermo, oggi ci troviamo di fronte al concetto di “Meatspace Layer”: un’infrastruttura dove le macchine non…
 Cybercrime
CybercrimeNegli ultimi anni, la sicurezza delle reti ha affrontato minacce sempre più sofisticate, capaci di aggirare le difese tradizionali e di penetrare negli strati più profondi delle infrastrutture. Un’analisi recente ha portato alla luce uno…
 Vulnerabilità
VulnerabilitàNegli ultimi tempi, la piattaforma di automazione n8n sta affrontando una serie crescente di bug di sicurezza. n8n è una piattaforma di automazione che trasforma task complessi in operazioni semplici e veloci. Con pochi click…
 Innovazione
InnovazioneArticolo scritto con la collaborazione di Giovanni Pollola. Per anni, “IA a bordo dei satelliti” serviva soprattutto a “ripulire” i dati: meno rumore nelle immagini e nei dati acquisiti attraverso i vari payload multisensoriali, meno…