
Nel mondo dell’intelligenza artificiale sentiamo spesso parlare di due termini, Machine Learning (ML) e Deep Learning (DL). Sono entrambi metodi per implementare l’AI attraverso l’addestramento o training di algoritmi di apprendimento automatico, che verrano poi utilizzati per fare predizioni sul futuro e prendere decisioni.
Queste due materie utilizzano approcci e hanno capacità e caratteristiche differenti. In questo articolo andremo ad esplorare le differenze tra i due e capire meglio come funzionano.
Il Machine Learning è la materia che si occupa della progettazione di algoritmi capaci di fare predizioni imparando pattern di dati passati. Un algoritmo di Machine Learning si differenzia da un “classico” algoritmo di informatica propri per come viene strutturato il problema.
In un algoritmo classico noi diamo alla macchina delle regole che questa deve seguire passo passo, per trasformare l’input in un output. Ad esempio un input potrebbe essere una lista di numeri [1, 2, 3, 4, 5], la regola potrebbe essere: “trasforma ogni numero nel suo quadrato”, quindi f(x) = x^2.
Una volta fornite queste regole e questo input, l’algoritmo sarebbe in grado di restituirci il seguente output: [1, 4, 9, 16, 25].
In un algorimto di Machine Learning invece il problema viene stravolto.
Quello che noi forniamo alla macchina è l’input e l’output atteso, quindi [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] e [1, 4, 9, 16, 25], e l’algoritmo ci restituirà in output la regola che mette in relazione questi valori, quindi f(x) = x^2.
In questo modo a noi non resta che preoccuparci principalmente di raccogliere delle osservazioni (dati) e darli in pasto all’algoritmo che troverà la relazione che regola le nostre osservazioni e che potrà essere usata per fare predizioni future.
Il tipo di algoritmo di Machine Learning appena descritto in realtà rientra nella categoria degli algoritmi definiti come Supervised Learning.
Esistono fondamentalmente 3 categorie differenti che sono le seguenti:
Esistono molti algoritmi di Machine Learning, ed è compito del data scientist capire quale usare e in quale occasione. Un algoritmo in particolare, chiamato Rete Neurale Artificiale, ha aperto numerose nuove possibiltà e gli scienziati dell’AI hanno iniziato a focalizzarsi sullo studio di questo singolo algoritmo, ed è cosi nata una nuova materia di studio chiamata Deep Learning.
Il Deep Learning è un sottoinsieme del Machine Learning, infatti si focalizza solamente sull’uso delle Reti Neurali Artificiali che sono in grado di imparare pattern nascosti all’interno dei dati.
La Rete Neurale Artificiale (ANN) è ispirata a quella biologica.
L’elemento di base di una rete neurale biologica è il singolo neurone, mentre in quella artificiale troviamo il percettrone. Il neurone percepisce attraverso i dendriti delle scariche elettrice in input che vengono processate dal nucleo, e se la somma di queste scariche supera una certa soglia verrà prodotta una scarica elettrica in output attraverso l’assone.
In modo simile il percettrone riceve in input dei numeri, esegue una computazione di questi numeri e produce un numero in output, 0 o 1. Ad esempio i numeri in input potrebbero rappresentare il valore dei pixel in un’ immagine in bianco e nero, e noi vorremmo che l’output sia 1 se l’immagine rappresenta un cane e zero altrimenti.
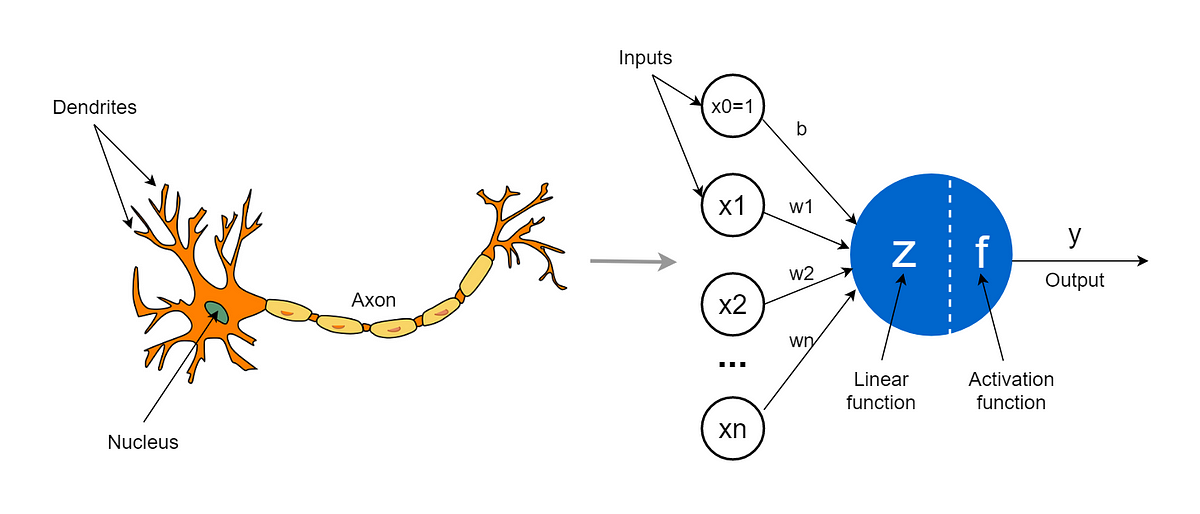
Il percettrone però è un algoritmo troppo semplice e ha poca capacità di apprendimento.
Quindi possiamo creare un algoritmo più complesso strutturando tanti percettroni (o neuroni) in layer in cui l’output dei neuroni nei layer precedenti saranno l’input per i layer successivi.
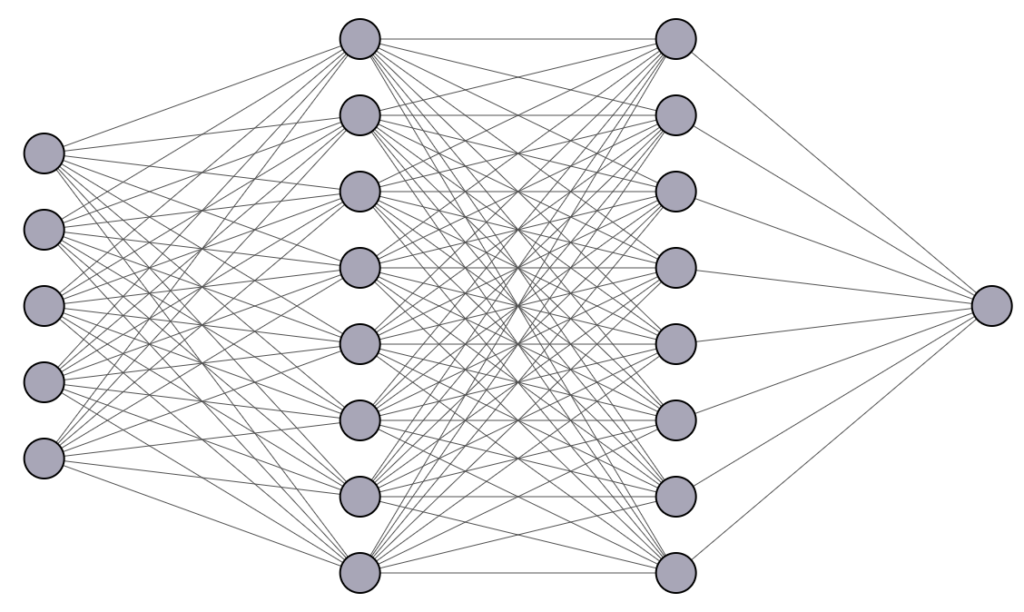
I layer in questa immagine sono solamente quattro. Abbiamo il primo input layer, seguito da due hidden layer e infine un output layer composto da un singolo neurone. Il numero di hidden layer è arbitrario e spesso le reti possono essere molto profonde, è per questo che si usa il termine deep.
Le reti neurali non si differenziano tra loro solo per il numero di neuroni o layer, ma anche per il tipo di computazione che questi layer e neuroni eseguono. Esistono vari tipi di reti neurali, come ad esempio le Reti Neurali Convoluzionali (CNN) adatte a task visuali, o le Reti Neurali Ricorrenti (RNN) per taks in cui si elaborano dati sequenziali come le serie storiche o il linguaggio naturale.
Ora che abbiamo visto gli aspetti principali del Machine Learning e del Deep Learning, andiamo a vedere quali sono le differenze tra i due e in quali casi bisogna prediligere uno a discapito dell’altro.
Il Machine Learning e il Deep Learning sono due approcci del campo dell’AI. Hanno entrambi punti di forza e di debolezza, e la scelta dipende dal problema da affrontare, dalla disponibilità di dati e dalla complessità del compito.
Comprendere le differenze tra queste due tecniche è fondamentale per i professionisti e i ricercatori nel campo dell’intelligenza artificiale per scegliere l’approccio più appropriato per i loro casi d’uso specifici.
Ti è piaciuto questo articolo? Ne stiamo discutendo nella nostra Community su LinkedIn, Facebook e Instagram. Seguici anche su Google News, per ricevere aggiornamenti quotidiani sulla sicurezza informatica o Scrivici se desideri segnalarci notizie, approfondimenti o contributi da pubblicare.
 Cybercrime
CybercrimeLe autorità tedesche hanno recentemente lanciato un avviso riguardante una sofisticata campagna di phishing che prende di mira gli utenti di Signal in Germania e nel resto d’Europa. L’attacco si concentra su profili specifici, tra…
 Innovazione
InnovazioneL’evoluzione dell’Intelligenza Artificiale ha superato una nuova, inquietante frontiera. Se fino a ieri parlavamo di algoritmi confinati dietro uno schermo, oggi ci troviamo di fronte al concetto di “Meatspace Layer”: un’infrastruttura dove le macchine non…
 Cybercrime
CybercrimeNegli ultimi anni, la sicurezza delle reti ha affrontato minacce sempre più sofisticate, capaci di aggirare le difese tradizionali e di penetrare negli strati più profondi delle infrastrutture. Un’analisi recente ha portato alla luce uno…
 Vulnerabilità
VulnerabilitàNegli ultimi tempi, la piattaforma di automazione n8n sta affrontando una serie crescente di bug di sicurezza. n8n è una piattaforma di automazione che trasforma task complessi in operazioni semplici e veloci. Con pochi click…
 Innovazione
InnovazioneArticolo scritto con la collaborazione di Giovanni Pollola. Per anni, “IA a bordo dei satelliti” serviva soprattutto a “ripulire” i dati: meno rumore nelle immagini e nei dati acquisiti attraverso i vari payload multisensoriali, meno…