
Cisco Talos ha identificato una nuova campagna ransomware chiamata DeadLock: gli aggressori sfruttano un driver antivirus Baidu vulnerabile (CVE-2024-51324) per disabilitare i sistemi EDR tramite la tecnica Bring Your Own Vulnerable Driver (BYOVD). Il gruppo non gestisce un sito di fuga di dati ma comunica con le vittime tramite Session Messenger.
Secondo Talos gli attacchi vengono eseguiti da un operatore motivato finanziariamente che ottiene l’accesso all’infrastruttura della vittima almeno cinque giorni prima della crittografia e prepara gradualmente il sistema per l’implementazione di DeadLock.
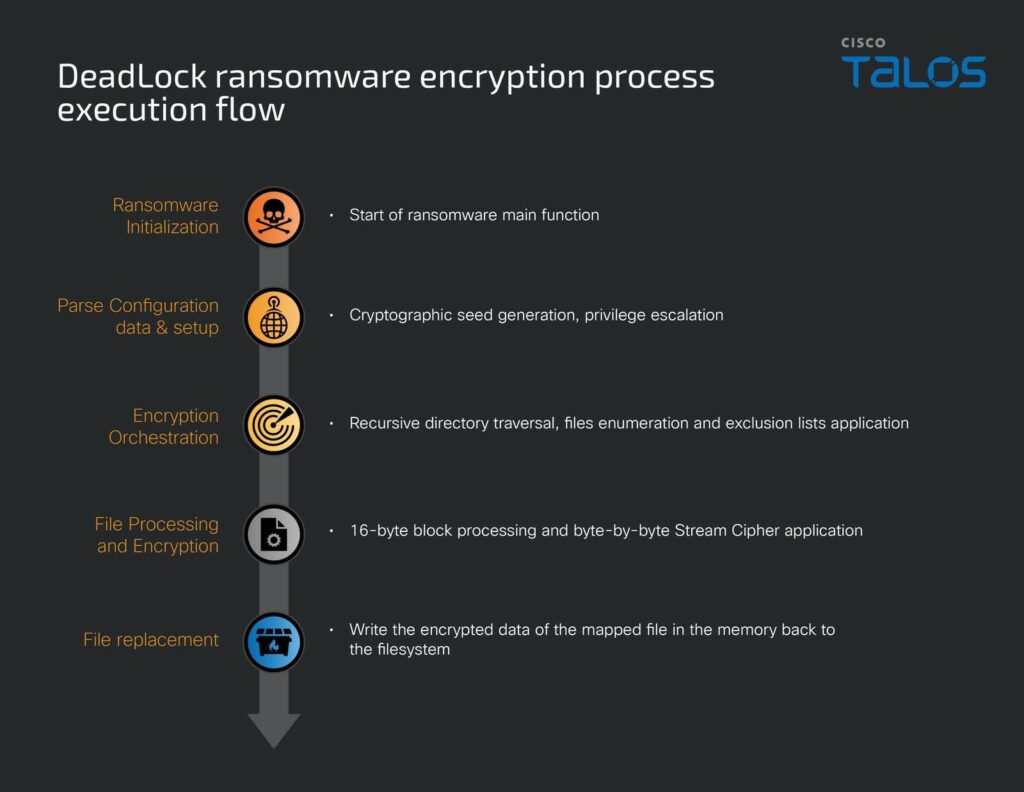
Uno degli elementi chiave della catena è BYOVD : gli aggressori stessi introducono nel sistema un driver Baidu Antivirus legittimo ma vulnerabile, BdApiUtil.sys, camuffato da DriverGay.sys, e il proprio loader, EDRGay.exe. Il loader inizializza il driver in modalità utente, stabilisce una connessione ad esso tramite CreateFile() e inizia a enumerare i processi alla ricerca di soluzioni antivirus ed EDR.
Successivamente, viene sfruttata la vulnerabilità CVE-2024-51324, un errore di gestione dei privilegi nel driver. Il loader invia uno speciale comando DeviceIOControl() al driver con codice IOCTL 0x800024b4 e il PID del processo di destinazione.
Dal lato kernel, il driver interpreta questo come una richiesta di terminazione del processo, ma a causa della vulnerabilità, non verifica i privilegi del programma chiamante. Eseguendo con privilegi kernel, il driver richiama semplicemente ZwTerminateProcess() e “termina” immediatamente il servizio di sicurezza, aprendo la strada ad ulteriori aggressori.
Prima di lanciare il ransomware, l’operatore esegue uno script PowerShell preparatorio sul computer della vittima. Innanzitutto, verifica i privilegi dell’utente corrente e, se necessario, si riavvia con privilegi amministrativi tramite RunAs, bypassando l’UAC e attenuando le restrizioni standard di PowerShell.
Dopo aver ottenuto i privilegi di amministratore, lo script disabilita Windows Defender e altri strumenti di sicurezza, arresta e disabilita i servizi di backup, i database e altri software che potrebbero interferire con la crittografia. Elimina inoltre tutti gli snapshot delle copie shadow del volume, privando la vittima degli strumenti di ripristino standard, e infine si autodistrugge, complicando l’analisi forense.
Lo script include anche un elenco dettagliato di eccezioni per i servizi critici per il sistema. Tra queste rientrano i servizi di rete (WinRM, DNS, DHCP), i meccanismi di autenticazione (KDC, Netlogon, LSM) e i componenti di base di Windows (RPCSS, Plug and Play, registro eventi di sistema).
Ciò consente agli aggressori di disabilitare il maggior numero possibile di componenti di sicurezza e applicativi senza causare l’arresto anomalo dell’intero sistema, consentendo alla vittima di leggere la nota, contattare il ransomware e pagare.
Talos ha notato che alcune sezioni dello script relative all’eliminazione delle condivisioni di rete e ai metodi alternativi per l’arresto dei processi erano commentate, a indicare che gli autori le intendevano come “opzioni” per scopi specifici. Lo script carica dinamicamente alcune eccezioni da un file run[.]txt esterno.
La telemetria indica che gli aggressori stanno accedendo alla rete della vittima tramite account legittimi compromessi. Dopo l’accesso iniziale, configurano l’accesso remoto persistente: utilizzando il comando reg add, modificano il valore di registro fDenyTSConnections per abilitare RDP. Quindi, utilizzando netsh advfirewall, creano una regola che apre la porta 3389, impostano il servizio RemoteRegistry in modalità on-demand e lo avviano, consentendo la gestione remota del registro.
Il giorno prima della crittografia, l’operatore installa una nuova istanza di AnyDesk su una delle macchine , nonostante altre installazioni del software siano già presenti nell’infrastruttura, rendendo questa distribuzione sospetta.
AnyDesk viene distribuito in modo silenzioso, con l’avvio di Windows abilitato, una password configurata per l’accesso silenzioso e gli aggiornamenti disabilitati che potrebbero interrompere le sessioni degli aggressori. Successivamente, inizia la ricognizione attiva e lo spostamento della rete: nltest viene utilizzato per trovare i controller di dominio e la struttura del dominio, net localgroup/domain per enumerare i gruppi privilegiati, ping e quser per verificare la disponibilità e gli utenti attivi, e infine mstsc e mmc compmgmt.msc per connettersi ad altri host tramite RDP o tramite lo snap-in Gestione Desktop remoto.
Il potenziale accesso alle risorse web interne viene rilevato dall’avvio di iexplore.exe con indirizzi IP interni.
Ti è piaciuto questo articolo? Ne stiamo discutendo nella nostra Community su LinkedIn, Facebook e Instagram. Seguici anche su Google News, per ricevere aggiornamenti quotidiani sulla sicurezza informatica o Scrivici se desideri segnalarci notizie, approfondimenti o contributi da pubblicare.
 Cybercrime
CybercrimeLe autorità tedesche hanno recentemente lanciato un avviso riguardante una sofisticata campagna di phishing che prende di mira gli utenti di Signal in Germania e nel resto d’Europa. L’attacco si concentra su profili specifici, tra…
 Innovazione
InnovazioneL’evoluzione dell’Intelligenza Artificiale ha superato una nuova, inquietante frontiera. Se fino a ieri parlavamo di algoritmi confinati dietro uno schermo, oggi ci troviamo di fronte al concetto di “Meatspace Layer”: un’infrastruttura dove le macchine non…
 Cybercrime
CybercrimeNegli ultimi anni, la sicurezza delle reti ha affrontato minacce sempre più sofisticate, capaci di aggirare le difese tradizionali e di penetrare negli strati più profondi delle infrastrutture. Un’analisi recente ha portato alla luce uno…
 Vulnerabilità
VulnerabilitàNegli ultimi tempi, la piattaforma di automazione n8n sta affrontando una serie crescente di bug di sicurezza. n8n è una piattaforma di automazione che trasforma task complessi in operazioni semplici e veloci. Con pochi click…
 Innovazione
InnovazioneArticolo scritto con la collaborazione di Giovanni Pollola. Per anni, “IA a bordo dei satelliti” serviva soprattutto a “ripulire” i dati: meno rumore nelle immagini e nei dati acquisiti attraverso i vari payload multisensoriali, meno…