Allarme rosso in Italia! Migliaia di impianti senza password: un incubo a portata di click
L’Italia si trova oggi davanti a una sfida digitale senza precedenti, dove la corsa all’innovazione non sempre coincide con una protezione adeguata delle infrastrutture. Pertanto la sicurezza dei sist...
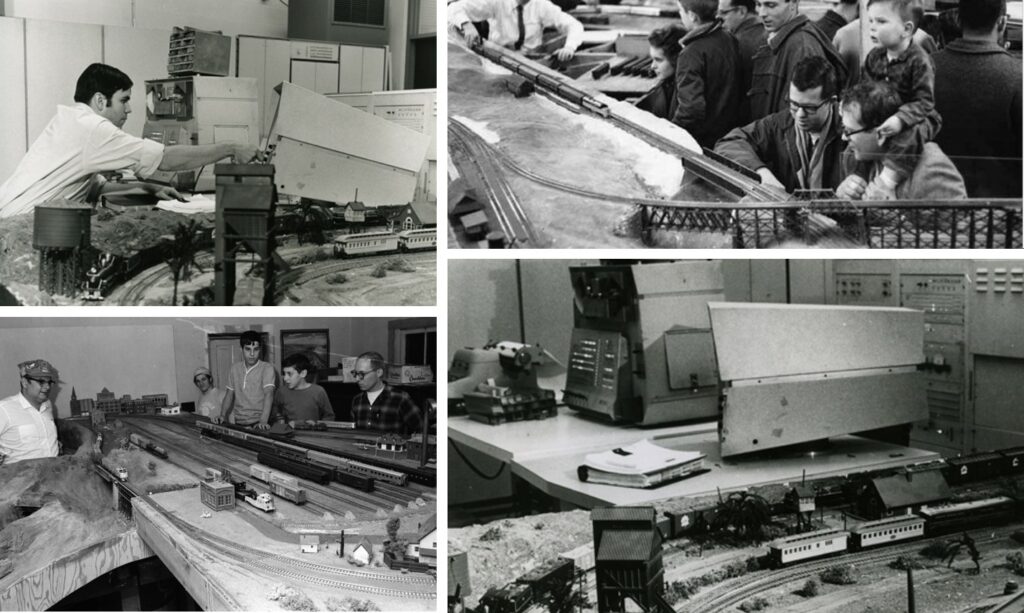
La vera storia degli hacker: dai trenini del MIT, alla voglia di esplorare le cose
La parola hacking, deriva dal verbo inglese “to hack”, che significa “intaccare”. Oggi con questo breve articolo, vi racconterò un pezzo della storia dell’hacking, dove tutto ebbe inizio e precisament...
Supply Chain Attack: come è stato compromesso Notepad++ tramite il CVE-2025-15556
Nella cyber security, spesso ci si concentra sulla ricerca di complessi bug nel codice sorgente, ignorando che la fiducia dell’utente finale passa per un elemento molto più semplice: un link di downlo...
Il “Reddit per AI” progetta la fine dell’umanità e crea una Religione. Ecco la verità su Moltbook
L’evoluzione delle piattaforme digitali ha raggiunto un punto di rottura dove la presenza umana non è più richiesta per alimentare il dibattito. Moltbook emerge come un esperimento sociale senza prece...
Initial Access Broker (IaB): Sempre più una comodity nei mercati underground
Nel mondo dell’underground criminale, il lavoro si divide tra “professionisti”. C’è chi sviluppa ed esercisce il ransomware, c’è chi vende un accesso iniziale alle aziende e c’è chi sfrutta l’accesso ...
Microsoft Office sotto attacco: il bug da patchare per evitare spionaggio russo
Negli ultimi giorni, APT28, noto gruppo di hacker legato alla Russia, ha intensificato gli attacchi sfruttando una vulnerabilità di Microsoft Office. La falla, catalogata come CVE‑2026‑21509, è stata ...
La governance dei flussi di dati tra Direttiva NIS 2 e responsabilità penale omissiva
Dopo aver analizzato nei precedenti contributi il perimetro dei reati informatici e i rischi legati alle manovre di difesa attiva, è necessario compiere un ultimo passo verso la comprensione della cyb...
Formazione avanzata in OSINT: la Polizia Postale rafforza le indagini nel cyberspazio
Si è concluso la scora settimana, presso la Scuola Allievi Agenti della Polizia di Stato di Vibo Valentia, il corso di formazione specialistica in OSINT – Open Source Intelligence, rivolto agli operat...
31,4 Tbps: quando il DDoS diventa “meteo” e l’IoT fa da grandine
Se vi state chiedendo quanto sia grande 31,4 terabit al secondo, la risposta pratica è: abbastanza da far sembrare “un problema di rete” quello che in realtà è un problema di ecosistema. Perché il pun...
BETTI RHC: il fumetto che educa alla cybersecurity. Esce il 4 e 5 episodio
BETTI RHC è un progetto editoriale e culturale ideato da Red Hot Cyber, realtà italiana punto di riferimento nel panorama della cybersecurity e della divulgazione tecnologica. Non si tratta di un semp...
Articoli più letti dei nostri esperti
Vulnerabilità critica in n8n: eseguiti comandi di sistema indesiderati
Redazione RHC - 5 Febbraio 2026
Training on the job: normativa, esempi e strumenti
Redazione RHC - 5 Febbraio 2026
Il 2026 sarà l’anno dell’industrializzazione del cybercrime
Marcello Filacchioni - 5 Febbraio 2026
Allarme rosso in Italia! Migliaia di impianti senza password: un incubo a portata di click
Bajram Zeqiri - 5 Febbraio 2026
Attacchi informatici tramite NGINX: una nuova minaccia per il traffico web
Redazione RHC - 5 Febbraio 2026
HackerHood di RHC scopre un nuovo 0day nei Firewall ZYXEL: il rischio è l’accesso Root
Redazione RHC - 5 Febbraio 2026
La vera storia degli hacker: dai trenini del MIT, alla voglia di esplorare le cose
Massimiliano Brolli - 5 Febbraio 2026
LibreOffice 26.2: la suite per ufficio open source si evolve
Carolina Vivianti - 5 Febbraio 2026
Impiegati infedeli: Ex Ingegnere Google rubava i segreti sulle AI per mandarli in Cina
Carolina Vivianti - 4 Febbraio 2026
L’Italia sotto Attacco Hacker! Dopo la Sapienza e gli Uffizi, NoName057(16) colpisce ancora
Redazione RHC - 4 Febbraio 2026
Ultime news
Vulnerabilità critica in n8n: eseguiti comandi di sistema indesiderati
Training on the job: normativa, esempi e strumenti
Il 2026 sarà l’anno dell’industrializzazione del cybercrime
Allarme rosso in Italia! Migliaia di impianti senza password: un incubo a portata di click
Attacchi informatici tramite NGINX: una nuova minaccia per il traffico web
HackerHood di RHC scopre un nuovo 0day nei Firewall ZYXEL: il rischio è l’accesso Root
Scopri le ultime CVE critiche emesse e resta aggiornato sulle vulnerabilità più recenti. Oppure cerca una specifica CVE